Boost your preparation for Class 10 exams with these important questions and answers in Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy (Geography). Get ready to ace your test!
Lifelines of National Economy Class 10 Exam - Top Important Questions and Answers
Q. No. 1) Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
i. The Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways connect _____.
a. Delhi-Silchar-Madurai and Gandhinagar
b. Delhi-Mumbai-Chennai and Kolkata
c. Kashmir-Kanyakumari
d. Srinagar-Kanyakumari-Bhopal and Allahabad
Ans. Option (b)
ii. Which of the following corridors links Srinagar and Kanyakumari?
a. North-South Corridor
b. East-West Corridor
c. North-East Corridor
d. South-West Corridor
Ans. Option (a)
iii. Match the following roads from column A with the organization responsible for their construction and maintenance from Column B
| Column A (Types of Road) | Column B (Organization) |
| A. Super Highways | I. Zila Parishad |
| B. National Highways | II. State Public Works Department |
| C. State Highways | III. Central Public Works Department |
| D. District Roads | IV. National Highway Authority of India |
a. A-I, B-II, C-III, D-IV
b. A-II, B-I, C-IV, D-III
c. A-IV, B-III, C-II, D-I
d. A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
Ans. Option (c)
iv. The National Highway 1 connects which of the following places in India?
a. Delhi-Amritsar
b. Delhi-Patiala
c. Delhi-Kashmir
d. Delhi-Lucknow
Ans. Option (a) [The historical Sher-Shah Suri Marg is called National Highway No.1, between Delhi and Amritsar.]
v. Roads linking a state capital with different district headquarters are known as _____.
a. National highways
b. District roads
c. State highways
d. Other roads
Ans. Option (c)
vi. Which of the following types of roads received special impetus under the Pradhan Mantri Grameen Sadak Yojana?
a. National highways
b. State highways
c. Rural roads
d. District roads
Ans. Option (c)
vii. Name the first water port which was made just after the independence.
a. Mumbai
b. Kandhla
c. Kocchi
d. Haldia
Ans. Option (b) [Kandla also known as the Deendayal Port]
viii. Which is the deepest landlocked and well-protected port in India?
a. Mumbai
b. Kandla
c. Vishakhapatnam
d. New Mangalore
Ans. Option (c)
ix. The second class mail includes which one of the following?
a. Book packets
b. Cards
c. Envelops
d. Invitation cards
Ans. Option (a)
x. What are the two components of trade?
a. Tariff and Non-Tariff
b. Transport and Time
c. Price and Cost
d. Export and Import
Ans. Option (d)
xi. Which of the following helps in the development of an international understanding of our culture and heritage?
a. Tourism
b. Tradition
c. Topography
d. Commerce
Ans. Option (a)
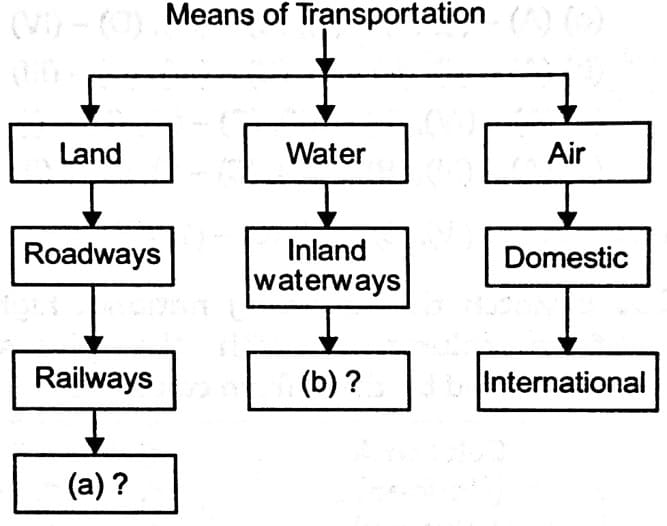
Q. No. 2) Complete the following table with appropriate terms in place of (a) and (b).
Ans. a – pipelines, b – overseas.
Q. No. 3) Read the extract and answer the questions that follow:
Today, the world has been converted into a large village with the help of efficient and fast-moving transport. Transport has been able to achieve this with the help of an equally developed communication system. Therefore, transport, communication, and trade are complementary to each other. Today, India is well-linked with the rest of the world despite its vast size, diversity, and linguistic and socio-cultural plurality. Railways, airways, waterways, newspapers, radio, television, cinema, and the internet, etc. have been contributing to its socio-economic progress in many ways. The trade from local to international levels has added to the vitality of its economy. It has enriched our life and added substantially to growing amenities and facilities for the comforts of life. It is thus, evident that a dense and efficient network of transport and communication is a prerequisite for local, national, and global trade of today.
i. Why is there a need to interlink with the world?
Ans. For development, advancement, and globalization
ii. Infer the importance of means of transportation and communication for socio-economic progress?
Ans. Importance of means of transportation and communication:
- They are the very basis of industries and trade in the country.
- Create job employment opportunities
- Help to grow economy
- Transport maintains the movement of persons and products from one region to another region of the country
- For sending and receiving messages
- Interlinking world
- Increases awareness among the people at the national level
- Help in defending the independence and the national unity of a country.
- Encourage national and international tourism.
iii. How does trade strengthen the economy of a country?
Ans. Importance of trade:
- Trade between nation and countries are the index to their economic prosperity.
- It generates employment.
- It Helps in earning foreign exchange.
Q. No. 4) Describe the benefits of Roadways.
Or,
India has one of the largest road networks in the world, aggregating about 2.3 million km at present. On what basis roadways have taken an edge over railways? Explain.
Or,
Compare and contrast the merits and demerits of roadways with those of railways.
Ans. Benefits of Roadways:
- Roads need less capital than railways.
- Road transport provides door-to-door service, thus the cost of loading and unloading is much lower
- Road transport provides flexible service to men and materials.
- Road transport is useful for small distances.
- Road transport is helpful in the production of perishable goods as it facilitates the distribution of perishable goods from point of production to point of consumption.
- Roads can negotiate higher gradients of slopes and as such can traverse mountains such as the Himalayas.
- Road transport is also used as a feeder to other modes of transport such as they provide a link between railway stations, air, and sea ports.
- The construction cost of roads is much lower than that of railway lines.
Q. No. 5) Classify roads into six classes according to their capacity.
Ans. Classification of Roads:
i. Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways:
- The government has launched a major road development project linking Kolkata-Chennai-Mumbai and Delhi by six-lane Super Highways.
- The North-South corridors linking Srinagar (Jammu & Kashmir) and Kanniyakumari (Tamil Nadu), and East-West Corridor connecting Silchar (Assam) and Porbandar (Gujarat) are part of this project.
- These highway projects are being implemented by the National Highway Authority of India (NHAI).
ii. National Highways:
- National Highways link extreme parts of the country.
- These are the primary road systems and are laid and maintained by the Central Public Works Department (CPWD).
- A number of major National Highways run in North-South and East-West directions.
- The historical Sher-Shah Suri Marg is called National Highway No.1, between Delhi and Amritsar.
iii. State Highways:
- Roads linking a state capital with different district headquarters are known as State Highways.
- These roads are constructed and maintained by the State Public Works Department (PWD).
iv. District Roads:
- These roads connect the district headquarters with other places in the district.
- These roads are maintained by the Zila Parishad.
v. Other Roads:
- Rural roads, which link rural areas and villages with towns, are classified under this category.
- These roads received special impetus under the Pradhan Mantri Grameen Sadak Yojana.
vi. Border Roads:
- Border roads are very significant for the security of the country.
- These roads are constructed and maintained by the Border Roads Organization.
- It has provided access to areas of difficult terrain.
- It helps in the economic development of the area.
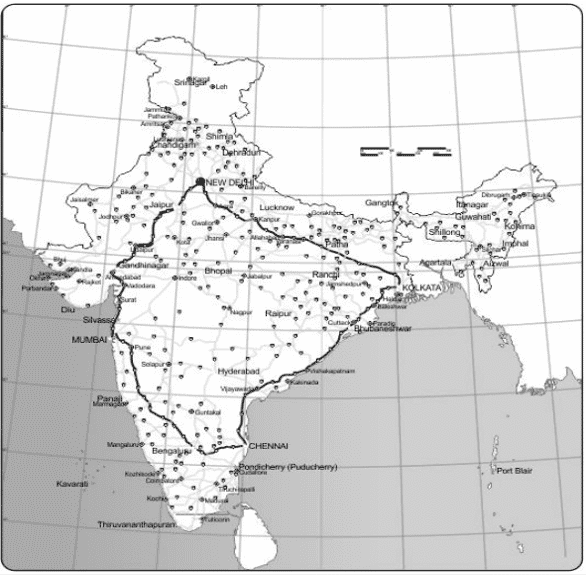
Q. No. 6) Identify the road development project from the map given below and briefly describe it.
Ans. Identification: It is the six-lane Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways project being implemented by NHAI.
Description
- Its main objective is to reduce the time and distance between the mega cities of India, namely Delhi-Mumbai-Kolkata-Chennai.
- The North-South corridor links Srinagar (Jammu & Kashmir) and Kanniyakumari (Tamil Nadu) while the East-West corridor links Silchar (Assam) and Porbandar (Gujarat).
Q. No. 7) What is the meaning of road density? Describe any four major problems faced by road transport in India.
Ans. Road Density: The length of road per 100 sq. km of area.
Problems faced by roadways:
- Keeping in view the volume of traffic and passengers the road network is inadequate.
- About half of the roads are unmetalled and this limits their usage during the rainy seasons.
- The national highways are inadequate too.
- Roads are highly congested in cities.
- Most of the bridges and culverts are old and narrow
Q. No. 8) Explain the importance of railways.
Or,
“Railways are the principal mode of transportation in India.” Explain.
Ans. Importance of railways:
- Railways are the principal mode of transportation for freight and passengers in India.
- It is convenient and safe to travel long distances by railway.
- Railways make it possible to conduct multifarious activities like business, sightseeing, and pilgrimage along with the transportation of goods over longer distances.
- Railways in India bind the economic life of the country.
- Railways accelerate the development of industry and agriculture.
- It provides employment to a large number of people.
Q. No. 9) Examine the factors that influence the distribution pattern of the railway network in India.
Ans. Physical and economic factors have influenced the distribution pattern of the Indian Railways network in the following ways:
- Northern Plain: Level land, high population density, and rich agricultural resources have favored the development of railways in these plains. However, a large number of rivers requiring the construction of bridges across their wide river beds posed some obstacles.
- Peninsular region and the Himalayan region: It is a hilly terrain. The railway tracks are laid through low hills, gaps, or tunnels. So, it is very difficult to lay the railway lines. The Himalayan mountainous regions too are not favorable for the construction of railway lines due to high relief, sparse population, and lack of economic opportunities.
- Desert of Rajasthan: On the sandy plain of western Rajasthan too, it is very difficult to lay railway lines which have hindered the development of railways.
- Swamps of Gujarat, and forested tracts of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Orissa, and Jharkhand; are also not suitable for the development of railways.
- The contiguous stretch of Sahyadri could be crossed only through gaps or passes. Although the Konkan railway along the west coast has been developed, it has also faced a number of problems such as the sinking of track in some stretches and landslides.
Q. No. 10) Why do you think the northern plains of India provide favorable conditions where as the Himalayan mountains provide unfavorable conditions for the growth of railways? Give three reasons for both.
Ans. Favorable conditions for the growth of railways in the Northern Plains
- Vast level land
- High population density
- Rich agricultural resources
Unfavorable conditions for the growth of railways in the Himalayan mountains
- High relief
- Sparse population
- Lack of economic opportunities
Q. No. 11) What are the problems being faced by the Indian railways?
Ans. The following problems are being faced by the railways:
- Many passengers travel without tickets which leads to revenue loss.
- Thefts and damage to railway property have not yet stopped completely.
- People stop the trains and pull the chain unnecessarily and this causes heavy damage to the railway.
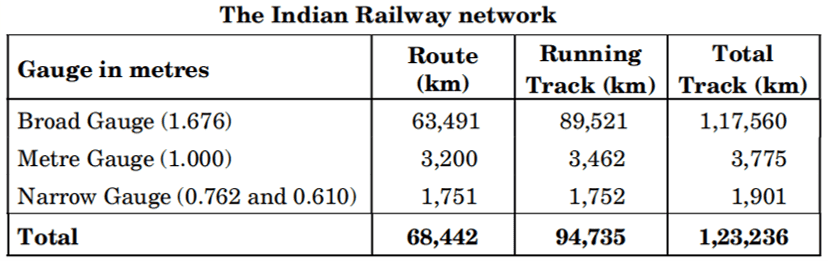
Q. No. 12) Read the following table and answer the questions that follow:
i. Which gauge covers the maximum track length in hilly areas in India?
ii. Which gauge has the highest length in India?
Ans. i. Since hilly areas have dissecting and undulating terrain, a narrow gauge would be an appropriate option.
ii. Broad gauge has the highest length of 1,17,560 km.
Q. No. 13) What is pipeline transportation? Write two merits and demerits of the same.
Ans. The pipeline transport network is the new mode of transport these days. In the past, pipelines were used to transport water to cities and industries. Now, these are used for transporting crude oil, petroleum products, and natural gas from oil and natural gas fields to refineries, fertilizer factories, and big thermal power plants. Solids can also be transported through a pipeline when converted into the slurry.
Merits
- Useful in transporting liquids and solid slurry from far away locations.
- Subsequent running costs after laying down the network are minimal.
- It rules out trans-shipment losses or delays.
- It saves time and reduces pressure on rail transport.
- Pipelines make transport fast, safe, and easy.
Demerits
- The initial cost of laying pipelines is high.
- Pipelines can burst or can have leakage leading to the wastage of valuable resources like water, mineral oil, etc.
Q. No. 14) Name the longest National Waterway in India. Mention any three importance of waterways in India.
Ans. The Ganga river between Allahabad and Haldia (National Waterway No. 1) is the longest National Waterway in India.
Importance of waterways in India:
- Cheapest means of transport.
- Most suitable for carrying heavy and bulky goods.
- Fuel-efficient and environmentally friendly mode of transport.
- They are natural routes that do not involve the cost of construction.
Q. No. 15) Explain the characteristics of Kandla Seaport.
Ans. Characteristics of Kandla seaport:
- Kandla in Kuchchh was the first port developed soon after Independence.
- It eased the volume of trade at the Mumbai port.
- Kandla, also known as the Deendayal Port, is a tidal port.
- It caters to the convenient handling of exports and imports of the highly productive granary and industrial states.
Q. No. 16) “Airways is the most preferred mode of transport in North-Eastern states of India.” Give three reasons to prove this preference.
Ans. Airways is the most preferred mode of transport in North-Eastern states of India because:
- The northeastern part of the country is marked by the presence of big rivers, dissected relief, and dense forests hence, it is difficult to construct roads and railway lines there.
- There are frequent floods and international frontiers, which require immediate and quick attention from the government authorities. Floods also damage roads and railway lines.
- Air travel has made access to the northeastern part of the country easier and quicker.
Q. No. 17) Analyze the significance of communication for a nation.
Ans. Significance of communication for a nation:
- This is the age of communication using the telephone, television, films, and the Internet.
- Even books, magazines, and newspapers are important means of communication.
- Various means of communication have connected the world closer.
- It is a source of entertainment and knowledge.
Q. No. 18) Mention the six mail channels introduced recently to facilitate quick delivery of mail.
Ans. They are
- Rajdhani Channel
- Metro Channel
- Green Channel
- Business Channel
- Bulk Mail Channel
- Periodical Channel.
Q. No. 19) Describe the role of mass communication in India.
Or,
Explain the importance of ‘Radio’ and ‘Television’ as effective means of mass communication in India.
Ans. Role of mass communication in India:
- Mass communication provides entertainment.
- Creates awareness among people about various national programs and policies. It includes radio, television, newspapers, magazines, books, and films.
- All India Radio (Akashwani) broadcasts a variety of programs in national, regional, and local languages
- Doordarshan broadcasts programs of entertainment, education, sports, etc. for people of different age groups.
- India publishes a large number of newspapers and periodicals annually
- Newspapers are published in about 100 languages and dialects to create awareness among people in different parts of the country.
- India produces short films; video feature films and video short films.
- Mass media creates awareness among people on various socio-economic and political issues.
Q. No. 20) “The pace of change has been rapid in modern times and has impacted the ways of communication as well.” In light of the given statement explain the role of a variety of means of communication that are used in India in the current times.
Ans. Means of Personal Communication in India –
- The Indian postal network is the largest in the world. It handles parcels as well as personal written communications. Cards and envelopes are considered first–class mail and are airlifted between stations covering both land and air. The second–class mail includes book packets, registered newspapers, and periodicals. To facilitate quick delivery of mail in large towns and cities, six mail channels have been introduced recently. They are called Rajdhani Channel, Metro Channel, Green Channel, Business Channel, Bulk Mail Channel, and Periodical Channel.
- India has one of the largest telecom networks in Asia. Excluding urban places, more than two-thirds of the villages in India have already been covered with Subscriber Trunk Dialling (STD) telephone facility. There is a uniform rate of STD facilities all over India. It has been made possible by integrating the development of space technology with communication technology.
Mass communication in India –
- All India Radio (Akashwani) broadcasts a variety of programs in national, regional, and local languages for various categories of people, spread over different parts of the country.
- Doordarshan, the national television channel of India, is one of the largest terrestrial networks in the world. It broadcasts a variety of programs from entertainment, and education to sports, etc. for people of different age groups.
- India publishes a large number of newspapers and periodicals annually. The largest numbers of newspapers published in the country are in Hindi, followed by English and Urdu.
- India is the largest producer of feature films in the world. It produces short films; video feature films and video short films. The Central Board of Film Certification is the authority to certify both Indian and foreign films.
Q. No. 21) Define the following terms:
-
Trade
-
International Trade
-
Favorable Balance of Trade
-
Unfavorable Balance of Trade
Ans. a. Trade: The exchange of goods among people, states, and countries is referred to as a trade.
b. International trade: Trade between two countries is called international trade.
c. Favourable balance of trade: When the value of export exceeds the value of imports, it is called a favorable balance of trade.
d. Unfavourable balance of trade: When the value of imports exceeds the value of exports, it is termed as an unfavorable balance of trade.
Q. No. 22) “Advancement of international trade of a country is an index to its economic prosperity”. Elaborate with examples.
Or,
Explain why international trade is considered the economic barometer for the country.
Ans. The advancement of International Trade in a country is an index to its economic prosperity:
- Trade between two countries through sea, air, or land route helps in the development of the country.
- No country can survive without International trade.
- Export and Import are the components of Trade.
- Commodities in export- agriculture and allied products, areas and minerals, gems and jewelry, etc.
- The commodities imported to India include Petroleum and its products, precious stores, chemicals, etc.
Q. No. 23) Why is tourism considered a trade?
Or,
Assam with its extensive tea gardens and high production of crude oil has a lot of potential for the growth of tourism. What values are associated with the promotion of tourism?
Ans. Tourism is considered a trade because:
- Foreign tourists’ arrival in the country contributes to foreign exchange.
- Many people are directly engaged in the tourism industry.
- Tourism provides support to local handicrafts and cultural pursuits.
- Tourists visit India for medical tourism, eco-tourism, adventure tourism, cultural tourism, and business tourism.
- It promotes national integration.
- It develops international understanding among countries.
Also, Watch the Detailed Explanation of Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy
Hope these questions were helpful to you in preparing this chapter for your exams. Please share this with your friends and do comment if you have any doubts/suggestions to share.