Embark on a journey to conquer Minerals and Energy Resources, Chapter 5 of Class 10 Social Science, with our comprehensive collection of key questions and answers. This meticulously crafted resource encompasses all the essential concepts and topics covered in the chapter, ensuring you are well-equipped to tackle any question that may arise.
In addition to the textbook questions, we have also included extra questions to challenge your understanding and prepare you for the upcoming CBSE 2023-24 board exams. To further enhance your learning experience, we have compiled a downloadable PDF version of the questions and answers, allowing you to study anytime, anywhere.
Embrace simplified geography and propel your exam preparation to new heights with our Minerals and Energy Resources Class 10 Key Questions and Answers.

| Subject | Social Science (Geography) |
| Class | 10 |
| Board | CBSE and State Boards |
| Chapter No. | 5 |
| Chapter Name | Minerals and Energy Resources |
| Type | Important Questions Answers |
| Session | 2023-24 |
| Weightage | 3-6 marks |
"The only limit to our realization of tomorrow will be our doubts of today."
- Franklin D. Roosevelt
Minerals and Energy Resources Class 10 Important Questions & Answers
Q. No. 1) Fill in the blanks:
- The toothbrush and tube containing paste are made up of plastic obtained from _________.
- The sparkle in some toothpaste comes from _________.
- In __________ rocks are the minerals deposited and accumulated in the strata?
- Ferrous minerals account for about ________ of the total value of production of metallic minerals.
- ________ rock consists of a single mineral.
- ________ is the basic raw material for the cement industry.
- __________ metal is obtained from Bauxite.
- ________ sands in Kerala are rich in thorium.
- __________ is used in electric and electronic industries due to its excellent dielectric strength and resistance to high voltage.
- ________ is the most popular coal in commercial use.
- The Badampahar mine in Mayurbhanj and Kendujhar district is situated in __________.
- In India, the Gulf of Khambhat, The Gulf of Kuchch, and the Gangetic delta provide ideal conditions for utilizing ________ energy.
- Iron ore is exported to Japan and South Korea via ____________ port.
- In _________ iron ore belt, Kudremukh mines are located.
- Larger occurrences of minerals in igneous and metamorphic rocks are found in _________.
- _________ is the largest bauxite producer in India.
Ans.
- Petroleum
- Mica
- Sedimentary
- Three-fourth
- Limestone
- Limestone
- Aluminium
- Monazite
- Mica
- Bituminous
- Odisha
- Tidal energy
- Vishakhapatnam.
- Bellari-Chitradurga-Chikkamagaluru-Tumakuru
- Lodes
- Odisha
Q. No. 2) Match the items in Column A with that in Column B.
| Column A (Resources) | Column B (Category) |
| A. Potash | i. Non-Ferrous Mineral |
| B. Tin | ii. Energy Resource |
| C. Manganese | iii. Non-metallic mineral |
| D. Coal | iv. Metallic mineral |
Ans. A-iii, B-i, C-iv, D-ii
Q. No. 3) i. Match the items in Column A with that in Column B.
| Column A | Column B |
| a. Odisha-Jharkhand belt | i. Karnataka |
| b. Durg-Bastar-Chandrapur belt | ii. Ratnagiri |
| c. Ballari-Chitradurga-Chikkamagaluru-Tumakuru belt | iii. Mayurbhanj |
| d. Maharashtra-Goa belt | iv. Chhattisgarh |
Ans. a-iii, b-iv, c-i, d-ii
ii. Observe the map given below showing the distribution of thermal and nuclear power plants across India.
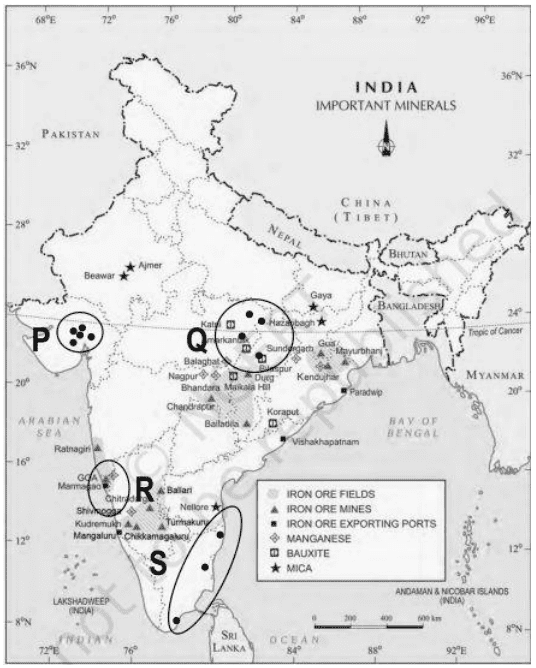
Air Quality Index (AQI) is used to measure real-time air pollution levels. A high AQI represents poor air quality.
Accordingly, which of the following regions marked on the map is LIKELY to experience comparatively better AQI?
a. P
b. Q
c. R
d. S
Ans. Option (c)
iii. Sharanya is making a list of natural resources for a project. She puts wind energy under one column and coal under another column.
On what basis is she classifying the resources?
a. on the basis of origin
b. on the basis of ownership
c. on the basis of exhaustibility
d. on the basis of status of development
Ans. Option (c)
Q. No. 4) Define mineral.
Ans. A mineral is a homogenous, naturally occurring substance with a definable internal structure.
Q. No. 5) Name the hardest and softest mineral.
Ans.
- Hardest: Diamond
- Softest: Talc
Q. No. 6) Name the iron ore which is the most important industrial iron ore in terms of the quantity used.
Ans. Hematite.
Q. No. 7) How do minerals occur in sedimentary rocks?
Ans. In sedimentary rocks, minerals occur in beds or layers. They have been formed as a result of deposition, accumulation, and concentration in horizontal strata.
Q. No. 8) Name any two minerals formed due to evaporation, especially in arid regions.
Ans. Gypsum, Potash salt, Sodium salt.
Q. No. 9) Explain three factors that make mineral extractions commercially viable.
Ans. Factors that make mineral extractions commercially viable are:
- The concentration of minerals in the ore.
- The ease of extraction
- Closeness to the market.
Q. No. 10) Differentiate between ferrous and non-ferrous minerals.
Ans.
| Ferrous minerals | Non-ferrous minerals |
| i. Minerals have iron content. | i. Minerals do not have iron content. |
| ii. They have in the development of metallurgical industries. | ii. They play an important role in a number of Engineering and electrical industries. |
| iii. Example: iron ore, manganese, etc. | iii. Example: lead, zinc, gold, etc. |
Q. No. 11) Which three places are connected with the HVJ gas pipeline?
Ans. Hazira, Vijaipur, and Jagdishpur.
Q. No. 12) Explain the reason why are mineral found in varied forms.
Ans. A particular mineral that will be formed from a certain combination of elements depends upon the physical and chemical conditions under which the material forms.
Q. No. 13) What are placer deposits? Give examples of minerals found in such deposits.
Ans. Certain minerals may occur as alluvial deposits in the sands of valley floors and the base of hills. These deposits are called placer deposits.
Gold, silver, tin, and platinum are found in such deposits.
Q. No. 14) Distinguish between Metallic minerals and Non-metallic minerals.
Ans.
| Metallic minerals | Non-metallic minerals |
| i. Metallic minerals are those which provide metal after processing such as iron, copper, aluminium, etc. | i. Non-metallic minerals are those which do not provide metals such as mica, potash, coal, limestone, etc. |
| ii. They are often hard. | ii. They are not so hard. |
| iii. They are generally associated with igneous rocks. | iii. They are generally associated with sedimentary rocks. |
| iv. They have a luster or shine of their own. | iv. They do not have a shine. |
| v. They are ductile and malleable. | v. They are not ductile and malleable. |
Q. No. 15) Give one point of difference between Magnetite and Hematite.
Ans.
- Magnetite: Finest iron ore, has up to 70% iron content.
- Hematite: Has a slightly lower iron content (50-60%).
Q. No. 16) Describe any three characteristics of the Orissa Jharkhand belt of iron ore in India.
Ans. Three characteristics of the Orissa Jharkhand belt of iron ore in India are:
- In Orissa, high-grade hematite ore is found
- It is found in Badampahar mines in the Mayurbhanj and Kendujhar districts.
- In the adjoining Singhbhum district of Jharkhand, hematite ore is mined in Gua and Noamundi.
Q. No. 17) Mention any four uses of manganese ore.
Ans. Uses of Manganese ore are:
- It is used in the manufacturing of steel and ferromanganese alloys.
- To manufacture bleaching powder.
- To manufacture insecticides.
- To manufacture paints.
Q. No. 18) Swamy visited a coal field at Neyveli along with his class X classmates as a school project last week. Name the type of coal found there.
Ans. Lignite coal.
Q. No. 19) How is bauxite formed? Give its uses. Discuss its distribution in India.
Ans. Formation: Bauxite deposits are formed by the decomposition of a wide variety of rocks rich in aluminium silicates.
Uses:
- Bauxite is a clay-like substance from which alumina and later aluminium are obtained.
- Aluminium is an important metal because it combines the strength of metals such as iron with extreme lightness and also with good conductivity and great malleability.
Distribution:
- Bauxite is found in the Amarkantak Plateau, Maikal Hills, and the plateau region of Bilaspur-Katni.
- Odisha is the largest bauxite-producing state in India.
Q. No. 20) Why is mica considered the most important mineral in electrical and electronic industries?
Ans. Mica is considered the most important mineral in electrical and electronic industries because:
- Excellent dielectric strength
- Low power loss factor
- Insulating properties
- Resistance to high voltage.
Q. No. 21) How has mining become a problem for workers and the environment?
Or,
Analyze the impact of mining activities on the local environment and the health of the surrounding communities.
Ans. Problems for miners:
- The miners have to work under tough conditions where no natural light is available.
- There is always a risk of collapse of the mine roof, inundation with water, and fire.
- Miners are at great risk of getting afflicted with pulmonary disorders.
Environmental Damage:
- The water sources in the region get contaminated due to mining.
- Dumping of waste and slurry leads to the degradation of land, and soil, and an increase in stream and river pollution.
Q. No. 22) What are the two main ways of generating electricity? How are they different from each other?
Ans. Two main ways of generating electricity:
- Hydroelectricity
- Thermal electricity.
| Thermal Electricity | Hydro Electricity |
| 1. It is obtained by using coal, petroleum, and natural gas. | 1. It is produced from water. |
| 2. It is a non-renewable resource. | 2. It is renewable. |
| 3. It causes pollution. | 3. It does not cause pollution. |
| 4. It is expensive in the long run. | 4. It is cheaper in the long run. |
Q. No. 23) Why should we conserve minerals? Suggest three ways to conserve minerals.
Ans. We need to conserve minerals because:
- The strong dependence of industry and agriculture upon mineral deposits and the substances manufactured from them.
- The geological processes of mineral formation are very slow.
- Mineral resources are finite and non-renewable.
- Continued extraction of ores leads to increasing costs as mineral extraction comes from greater depths along with a decrease in quality.
Ways to conserve minerals:
- A concerted effort has to be made in order to use mineral resources in a planned and sustainable manner.
- Improved technologies need to be constantly evolved to allow the use of low-grade ores at low costs.
- Recycling of metals, using scrap metals and other substitutes.
Q. No. 24) Explain the difference between conventional and non-conventional sources of energy. Name the two most common conventional resources used in rural India. Why the use of these conventional sources are discouraged?
Ans.
| Conventional source of energy | Non-conventional source of energy |
| 1. These are the traditional sources of energy produced from coal, petroleum, and natural gas. | 1. These are the sources of energy developed recently from the sun, wind, tide, etc. |
| 2. They are non-renewable. | 2. They are renewable. |
| 3. Their generation is expensive. | 3. Their generation is cheaper. |
| 4. They pollute the atmosphere on a large scale. | 4. They are pollution-free/less pollution sources. |
| 5. Example: coal, petroleum, natural gas, etc. | 5. Example: Solar energy, wind energy, tidal power, etc. |
- Firewood and cattle dung cake are most common in rural India. More than 70% energy requirement of rural households is met by these two.
- Continual use of firewood is increasingly becoming difficult due to decreasing forest area. Using dung cake is discouraged because it consumes the most valuable manure which could be used in agriculture.
Q. No. 25) Which minerals are used to obtain nuclear energy? How is nuclear energy obtained? Mention the names of all six nuclear power stations in India.
Ans. Uranium and Thorium are used to obtain nuclear energy.
Nuclear energy is obtained by altering the structure of atoms. When such an alteration is made, much energy is released in the form of heat and this is used to generate electric power.
Six nuclear power stations are:
- Naraura Power Plant in Uttar Pradesh
- Rawat Bhata Power Plant in Rajasthan
- Kakrapara Power Plant in Gujarat
- Tarapur Power Plant in Maharashtra
- Kaiga Power Plant in Karnataka
- Kalpakkam Power Plant in Tamil Nadu
Q. No. 26) How can solar energy solve the energy problem to some extent in India?
Ans. Solar energy can solve the energy problems to some extent in India:
- India is a tropical country therefore it receives sunlight in abundance throughout the year.
- Solar plants can be easily established in rural and remote areas.
- It will minimize the dependence of rural households on firewood and dung cakes which in turn will contribute to environmental conservation and adequate quantity of manure.
Q. No. 27) Define geothermal energy. Also mention two projects which have been set in India to harness geothermal energy.
Ans. Geothermal energy refers to the heat and electricity produced by using the heat from the interior of the Earth. Geothermal energy exists because the Earth grows progressively hotter with increasing depth.
Two experimental projects have been set up in India to harness geothermal energy:
- One is located in the Parvati valley near Manikarn in Himachal Pradesh.
- The other is located in the Puga Valley, Ladakh.
Q. No. 28) ‘There is a pressing need to use non-conventional energy sources in India.’ Analyze the statement with reasons.
Or,
“Non-conventional resources are the best option to conserve the natural resources” Substantiate this statement with Examples.
Ans. There is a pressing need to use non-conventional sources of energy in India:
- Because of the growing consumption of energy, the country is becoming increasingly dependent on fossil fuels.
- Rising prices of oil and gas and their potential shortages have raised uncertainties about the security of the energy supply in the future.
- These can have serious repercussions on the growth of the national economy.
- Increasing the use of fossil fuels also causes environmental problems.
Q. No. 29) Name the most abundantly available fossil fuel in India. Evaluate the importance of its different forms.
Ans. The most abundantly available fossil fuel in India is coal.
Forms of Coal:
- Peat: It has low carbon and high moisture content and low heating capacity.
- Lignite: It is low-grade brown coal that is soft with high moisture content. It is used for generating electricity.
- Bituminous: It is the most popular coal for commercial use. It has a special value for smelting iron in blast furnaces.
- Anthracite: It is the highest quality hard coal.
Q. No. 30) Highlight the importance of petroleum. Explain the occurrence of petroleum in India.
Ans. Importance of petroleum:
- It provides fuel for heat and lighting
- It provides lubricants for machinery
- It provides raw materials for a number of manufacturing industries.
- Petroleum refineries act as a ‘nodal industry’ for synthetic textile, fertilizer, and numerous chemical industries.
Occurrence of petroleum:
- Most of the petroleum occurrences in India are associated with anticlines and fault traps in the rock formations of the tertiary age.
- In regions of folding, anticline, or domes, it occurs where oil is trapped in the crest of the upfold.
- Petroleum is also found in fault traps between porous and non-porous rocks.
Q. No. 31) Which are the potential sources of biogas? State any four benefits of biogas.
Ans. Potential sources of biogas: Shrubs, farm waste, animal waste, human waste, etc.
Benefits of biogas:
- High thermal efficiency in comparison to kerosene, dung cake, and charcoal.
- It burns without smoke, causing no pollution.
- It is the most efficient use of cattle dung.
- It improves the quality of manure and also prevents the loss of trees and manure due to the burning of fuel wood and cow dung cakes.
Q. No. 32) Gobar Gas plants in rural India provide which twin benefits to the farmers?
Ans.
- Provision of energy
- Improved quality of manure.
Q. No. 33) Distinguish between natural gas and biogas.
Ans.
| Natural gas | Biogas |
| 1. It is a conventional source of energy. | 1. It is a non-conventional source of energy obtained from the decomposition of shrubs, farm waste, and animal and human wastes. |
| 2. It is used as a raw material in the petrochemical industry. | 2. It is used as fuel and for lighting homes. |
| 3. It is mainly used in urban areas. | 3. It is mainly used in rural areas. |
| 4. It is non-renewable. | 4. It is renewable. |
| 5. It is not environmentally friendly. | 5. It is environmentally friendly. |
Q. No. 34) Explain the need to adopt a cautious approach for the judicious use of our limited energy resources.
Ans. The need to adopt a cautious approach for the judicious use of our limited energy resources:
- Energy is a basic requirement for economic development. Every sector of the national economy like agriculture, industry, transport, commercial, and domestic needs inputs of energy.
- India is presently one of the least energy-efficient countries in the world. There is an urgent need to develop a sustainable path of energy development.
- Various development plans require increasing amounts of energy to remain operational. The success of economic development plans depends on energy resources.
Q. No. 35) Suggest ways to conserve energy resources in India.
Ans. Ways to conserve energy resources are:
- We have to adopt a cautious approach to the judicious use of our limited energy resources.
- Using public transport systems instead of individual vehicles.
- Switching off electricity when not in use.
- Using power-saving devices
- Using non-conventional sources of energy.
Q. No. 36) How is tidal energy generated?
Ans. Floodgate dams are built across inlets. The water flows into the inlet during high tide and gets trapped when the gate is closed. Once the tide recedes, the gates are opened so that water can flow back to the sea/ocean. The flow of water is used to run the turbine to generate electricity.
Q. No. 37) Which are the two planks of sustainable energy?
Ans. Promotion of energy conservation and increased use of renewable energy resources.
| Must Read: Minerals and Energy Resources Class 10 Notes Minerals and Energy Resources Class 10 NCERT Underlined PDF |
Hope you liked these Important Questions Answers on Minerals and Energy Resources Class 10 Geography. Please share this with your friends and do comment if you have any doubts/suggestions to share.
Sir aap ki wajah se tayari hamari achi chal rhi hai aap se request hai ki history 5 chapter yani print culture wala chapter kab upload karenge??? 🙏🙏
Video already upload ho chuka hai. Important questions and answers jald hi upload ho jayega iss website pe.
Sir manufacturing industries show nhi horha
Its uploaded just now. Please check now. https://www.cbseguidanceweb.com/print-culture-and-the-modern-world-class-10-important-questions-and-answers/
Mujhe ye sab questions ko pdf me chahiye sir jii
Sir aap please jaldi se nationalism in India ka important question answer upload kar dijiye
Bilkul Kal tak mil jayega
Sir sst ka paper hai some advice student
Abhi 1 day me kuch naya mat study karo. Jo bhi study kiye ho abhi tak usko hi revise karo. Bas yehi tip hai abhi ke liye.
Is the whole material like fill ups and question answers not available in pdf format?
No, currently all important QnAs are provided here in the website. You can take prinout from here itself and study.
Sir manufacturing industries aur lifelines of national economy ka extra questions chayiye
Plz upload kardijiye
sir can you please post ch7 of geography chapter
sir pls upload ss remaining chapters and maths important questions
Sir please tell me important chapters of history , civics , economics and geography to score 80percent in sst as i cant remember some chapters from geography like minerals and energy resources and manufacturing industries.
Hey!
Please add year no. Too
Pls sir all geography ch pls send me all important question
Class 10 Important Questions
Good afternoon sir,
Sir pls tell me…how many sample papers I should do to score in 70s or above..??