Are you ready to tackle Carbon and Its Compounds, the captivating Chapter 4 of your Class 10 science journey? Whether you're aiming for a perfect score in your upcoming CBSE board exams or simply seeking to solidify your understanding of this fundamental chemistry concept, this blog post is your ultimate guide.
We've meticulously compiled a comprehensive collection of Carbon and Its Compounds Class 10 important questions with detailed answers, all conveniently packaged in an easily downloadable PDF format. This invaluable resource will equip you with the knowledge and strategies to conquer even the most challenging questions.
But that's not all! To further enhance your exam preparation, we've included a bonus section of extra questions with detailed solutions. These practice questions will provide you with ample opportunities to test your understanding and refine your problem-solving skills, leaving no stone unturned as you prepare for exam success.
So, what are you waiting for? Embark on your Carbon and Its Compounds mastery journey today and confidently ace your Class 10 exams!
| Subject | Science (Chemistry) |
| Class | 10 |
| Board | CBSE & State Boards |
| Chapter No. | 4 |
| Chapter Name | Carbon and its Compounds |
| Type | Important Questions & Answers |
| Session | 2024-25 |
"The difference between ordinary and extraordinary is that little extra."
- Jimmy Johnson
Carbon and its Compounds Class 10 Important Questions & Answers
Q. No. 1) Fill in the blanks:
a. An atom or a group of atoms that is responsible for the chemical characteristics of an organic compound is called ________.
b. The general molecular formula of alkynes is ________.
c. (Saturated/Unsaturated) ________ compounds decolorize bromine water.
d. Dehydration of ethanol by conc. Sulphuric acid forms ________ (ethene/ethane).
e. 100% pure ethanol is called ________.
f. Ethanoic acid turns ________ litmus to ________.
Ans. a. Functional group
b. CnH2n-2
c. Unsaturated
d. Ethene.
e. Absolute alcohol
f. Blue, red.
Q. No. 2) Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
i. One mole of which of the following compounds requires 2 moles of hydrogen to form a saturated hydrocarbon by catalytic hydrogenation?
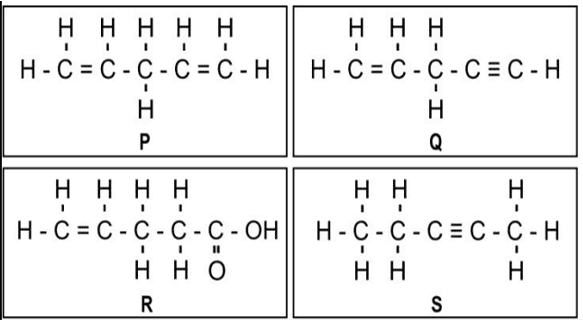
a. Only P and Q
b. Only R and S
c. Only P and S
d. Only P, Q, and S
Ans. Option (c) [2 moles of hydrogen means 2H2 = 4 atoms of hydrogen]
ii. Which of the following structures correctly represents the electron dot structure of a Nitrogen molecule?
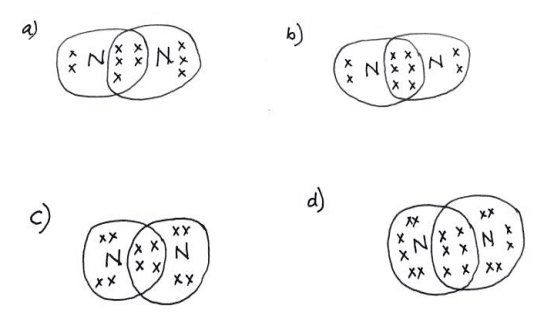
Ans. Option (b)
iii. Two statements are given – one labeled Assertion (A) and the other labeled Reason (R). Select the correct answer from the option given below.
(a) Assertion (A): Following are the structural isomers of butane.
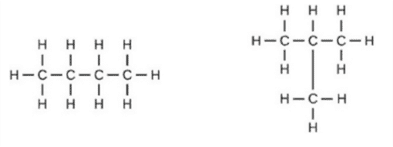
Reason (R): Structural isomers have the same molecular formula but they differ in their structures.
a. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c. A is true but R is false.
d. A is false but R is true.
Ans. Option (a)
iv. Assertion (A): Detergents are more effective cleansing agents than soaps in hard water.
Reason (R): Calcium and magnesium salts of detergents are water-soluble.
a. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c. A is true but R is false.
d. A is false but R is true.
Ans. Option (a)
v. The soap molecule has a
a. Hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail
b. Hydrophobic head and a hydrophilic tail
c. Hydrophobic head and a hydrophobic tail
d. Hydrophilic head and a hydrophilic tail
Ans. Option (a).
vi. In the soap micelles
a. The ionic end of soap is on the surface of the cluster while the carbon chain is in the interior of the cluster.
b. Ionic end of soap is in the interior of the cluster and the carbon chain is out of the cluster.
c. Both the ionic end and carbon chain are in the interior of the cluster.
d. Both the ionic end and carbon chain are on the exterior of the cluster.
Ans. Option (a)
Q. No. 3) The formulae of four organic compounds are given below:
A – C2H4
B – CH3COOH
C – C2H5OH
D – C2H6
(i) Which one of these compounds A, B, C, or D is a saturated hydrocarbon?
(ii) Identify the organic acid and give its structural formula.
(iii) Which of the above compounds when heated at 443K in the presence of conc. H2SO4 forms ethene as the major product? What is the role played by conc. H2SO4 in this reaction? Also, write the chemical equation involved.
(iv) Give a chemical equation when B and C react with each other in presence of conc. H2SO4. Name the major product formed and mention one of its important use.
Ans. (i) D is a Saturated hydrocarbon. (Note: Here B and C are also saturated carbon compounds, but in the question, they have asked for 'hydrocarbon', so the answer is D)
(ii) B is an organic acid.
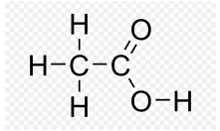
(iii) The compound is C (Ethanol). Conc. H2SO4 acts as a dehydrating agent which removes water from ethanol.
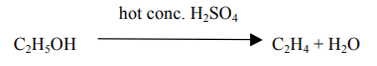
(iv)
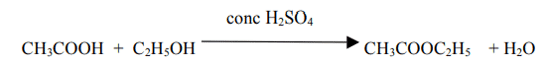
The major product is Ester (Ethyl ethanoate). It is used in making perfumes and as a flavoring agent.
Q. No. 4) Give the balanced chemical equation of the following reactions:
i. Neutralization of NaOH with ethanoic acid.
ii. Evolution of carbon dioxide by the action of ethanoic acid with NaHCO3.
iii. Oxidation of ethanol by acidified potassium dichromate.
iv. Combustion of ethanol.
Ans. i. NaOH + CH3COOH → CH3COONa + H2O
ii. CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
iii.
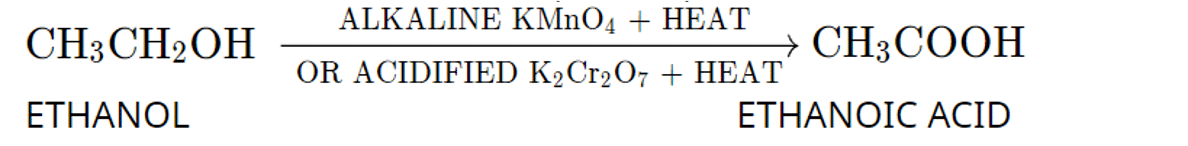
iv. C2H5OH + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O
Q. No. 5) Butter does not decolorize bromine water, whereas cooking oil does. Comment.
Ans. Unsaturated hydrocarbons decolorize bromine water. Therefore cooking oil decolorizes bromine water whereas butter does not.
Q. No. 6) An organic compound ‘A’ is widely used as a preservative and has the molecular formula C2H4O2. This compound reacts with ethanol to form a sweet-smelling compound ‘B’.
i. Identify the compound ‘A’.
ii. Write the chemical equation for its reaction with ethanol to form compound ‘B’.
iii. Name the process.
Ans. (i) A is Ethanoic acid.
(ii)
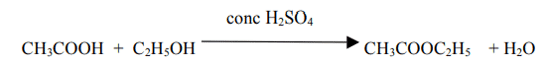
B is an ester (ethyl ethanoate).
(iii) Esterification reaction.
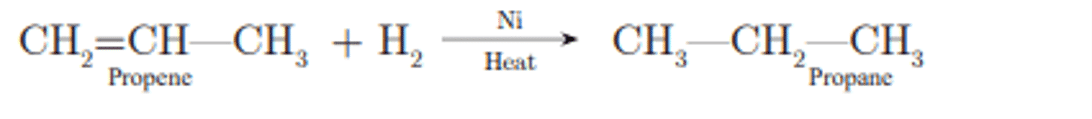
Q. No. 7) Write the name and formula of the 2nd member of the homologous series having the general formula CnH2n.
Ans. Propene, CH2=CH-CH3.
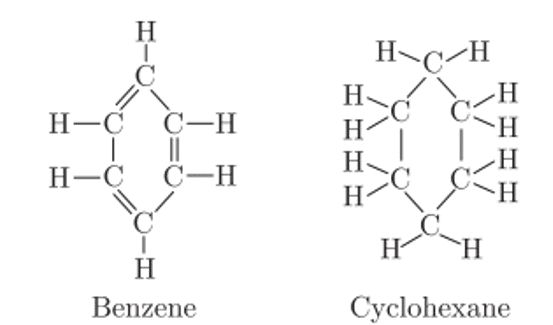
Q. No. 8) Compare the structures of benzene and cyclohexane by drawing them.
Ans. Benzene has 3 double bonds whereas cyclohexane has all single bonds.
Q. No. 9) Write the next homologue of propanol CH3CH2CH2OH and butanal CH3CH2CH2CHO.
Ans. CH3CH2CH2CH2OH Butanol
CH3CH2CH2CH2CHO Pentanal
Q. No. 10) State reasons to explain why covalent compounds:
a. Are bad conductors of electricity?
b. Have low melting and boiling points?
Ans. a. Covalent compounds do not form ions, hence they are bad conductors of electricity.
b. The forces of attraction between the molecules are not very strong. Hence, covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points.
Q. No. 11) What is hydrogenation? What is its industrial application?
Ans. Hydrogenation is a process of adding hydrogen to unsaturated compounds in presence of a catalyst like nickel or palladium to form saturated hydrocarbons.
Industrially, this reaction is used to convert vegetable oils to vegetable ghee.
Q. No. 12) List in tabular form three physical and two chemical properties on the basis of which ethanol and ethanoic acid can be differentiated.
Ans.
| Ethanol | Ethanoic Acid |
| (Difference in Physical properties) | |
| 1. It exists only in liquid form. | 1. It can exist both in liquid and solid form. |
| 2. Functional group is alcohol. | 2. Functional group is carboxylic acid. |
| 3. It has a specific smell but not like vinegar. | 3. It smells like vinegar. |
| (Difference in Chemical properties) | |
| 4. Does not react with sodium bicarbonate. | 4. Reacts with sodium bicarbonate to form salt, carbon dioxide, and water. |
| 5. No effect on litmus paper. | 5. It turns blue litmus paper red. |
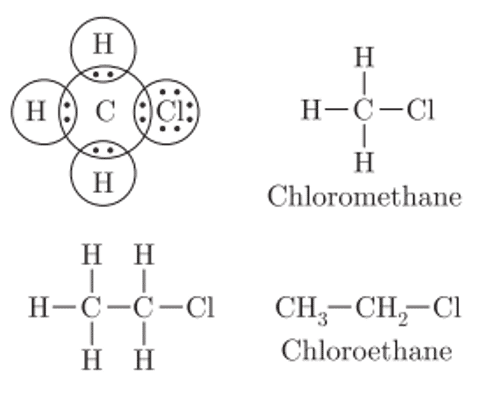
Q. No. 13) Give the electron dot structure of chloro-methane. Also, write the formula and the name of the next homologue of it.
Ans.
Q. No. 14) Two carbon compounds ‘X’ and ‘Y’ have the molecular formula C3H6 and C4H10 respectively. Which one of the two is most likely to show addition reaction? Justify your answer. Also, give a chemical equation to explain the process of addition in this case.
Ans. C3H6 will undergo an addition reaction because it has a double bond (unsaturated).
Q. No. 15) What will you observe on adding a 5% alkaline KMnO4 solution drop by drop to some warm ethanol taken in a test tube? Write the name of the compound formed during the above chemical reaction.
Ans. The purple color of KMnO4 decolorizes and ethanoic acid will be formed.
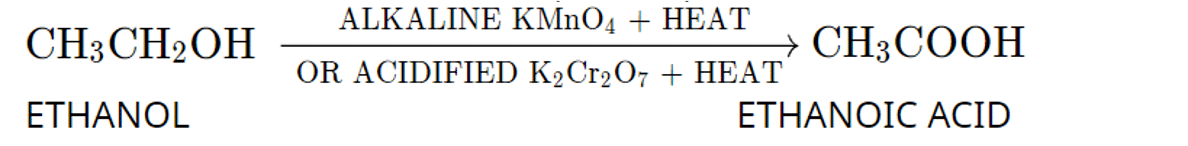
Q. No. 16) Prasad has a saturated alcohol X of chemical formula C4H9OH.
a. Write the chemical formula of a member Y that comes two places after X in the homologous series and state by how much will its molecular mass differ from that of X.
b. How do the chemical properties of X compare with those of Y? Give a reason for your answer.
c. Write the chemical formula of the product Z formed by heating Y with acidified potassium dichromate. Write the general formula for compounds in the homologous series that Z belongs to.
Ans. a. Chemical formula of Y is C6H13OH.
Difference between the molecular mass of successive compounds = 14 u
∴ Difference between the molecular mass of Y and X = 2 x 12 = 28 u
b. The chemical properties of X and Y will be similar. This is because both X and Y belong to the alcoholic functional group which determines their chemical properties.
c. C6H13OH + Acidified Potassium Dichromate → C5H11COOH Or C6H12O2 (Z)
The chemical formula of Z is C5H11COOH Or C6H12O2.
The general formula is CnH2n+1COOH Or CnH2nO2.
Q. No. 17) A compound has the molecular formula C2H6O. It can be used as fuel. Identify the name of the compound and the functional group present in it. Write the reaction involved in the conversion of this compound into Ethanoic acid.
Ans. The compound is Ethanol (C2H5OH). The functional group is –OH (alcohol).
Q. No. 18) An unsaturated hydrocarbon P has the chemical formula C4H6.
a. Write two possible structural formulae for hydrocarbon P.
b. Write the reaction conditions to convert 1-butanol (CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2OH) to hydrocarbon P.
c. Write the general formula for the homologous series of hydrocarbon P.
Ans. a. Structural isomers of C4H6 are
- HC ≡ C - CH2 - CH3
- H3C - C ≡ C - CH3
- H2C = C = CH - CH3
- H2C =CH - CH =CH2
b. Heating 1-butanol with excess hot concentrated sulphuric acid results in dehydration.
c. CnH2n-2
Q. No. 19) Given below is a four-carbon skeleton of a hydrocarbon compound.
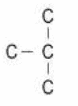
(a) Fill in the hydrogen atoms/bonds to form:
(i) a saturated hydrocarbon
(ii) an unsaturated hydrocarbon
(b) If the four-carbon skeleton is of a straight-chained alkene, draw the structures of all the possible compounds.
Ans. a. i.
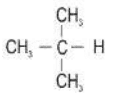
ii.
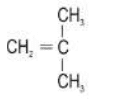
b. H3C-CH2-CH=CH2, H3C-CH=CH-CH3
Q. No. 20) What is denatured alcohol? Why is ethanol denatured? State any two uses of ethanol.
Ans. Ethanol when mixed with toxic substances like methanol is known as denatured alcohol.
Ethanol is denatured to make it unfit for drinking purposes so that alcohol for industrial purposes is not misused.
Uses of Ethanol:
- Ethanol is used to make cough syrups, tincture of iodine, etc.
- It is also used as a fuel as an additive to petroleum.
Q. No. 21) Raina while doing certain reactions observed that heating of substance ‘X’ with vinegar-like smell with a substance ‘Y’ (which is used as an industrial solvent) in the presence of conc. Sulphuric acid in a water bath gives a sweet-smelling liquid ‘Z’ having molecular formula C4H8O2. When heated with caustic soda (NaOH), ‘Z’ gives back the sodium salt of and the compound ‘Y’.
Identify ‘X’, ‘Y’, and ‘Z’. Illustrate the changes with the help of suitable chemical equations.
Ans.
X - Ethanoic acid/ acetic acid/ CH3COOH
Y - Ethanol/ Ethyl alcohol/ C2H5OH
Z - Ethyl ethanoate/ Ester – CH3COOC2H5
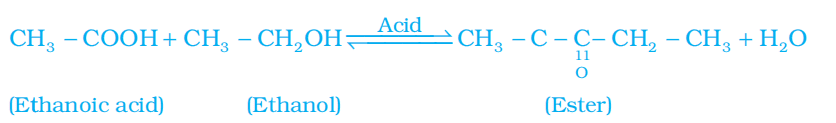
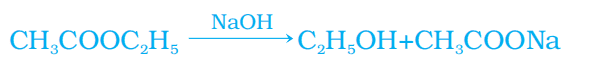
Q. No. 22) Differentiate between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Ans.
| Saturated Hydrocarbons | Unsaturated Hydrocarbons |
| 1. Compounds of carbon having only a single bond between their carbon atoms are called saturated hydrocarbons. | 1. Compounds of carbon having double or triple bonds between their carbon atoms are called unsaturated hydrocarbons. |
| 2. Less reactive than unsaturated hydrocarbons. | 2. More reactive than saturated hydrocarbons. |
| 3. General formula is CnH2n+2. | 3. General formula is CnH2n or CnH2n-2. |
| 4. It burns with a clean flame. | 4. It burns with a yellow sooty flame. |
| 5. Substitution reaction is the characteristic property of these hydrocarbons. | 5. Addition reaction is the characteristic property of these hydrocarbons. |
Q. No. 23) Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
Ans.
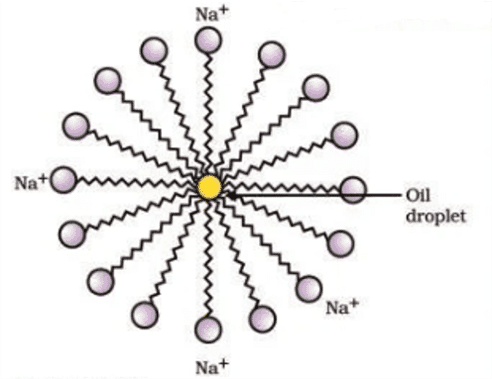
Most dirt is oily in nature and oil does not dissolve in water. The molecules of soap are sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids. The ionic end of soap interacts with the water while the carbon chain interacts with oil. The soap molecules, thus form structures called micelles where one end of the molecules is towards the oil droplet while the ionic end faces outside. This forms an emulsion in water. The soap micelle thus helps in pulling out the dirt in water and we can wash our clothes clean.
Q. No. 24) You are given the balls and sticks models of six carbon atoms and fourteen hydrogen atoms and a sufficient number of sticks. In how many ways one can join the models of six carbon atoms and fourteen hydrogen atoms to form different molecules of C6H14.
Ans.
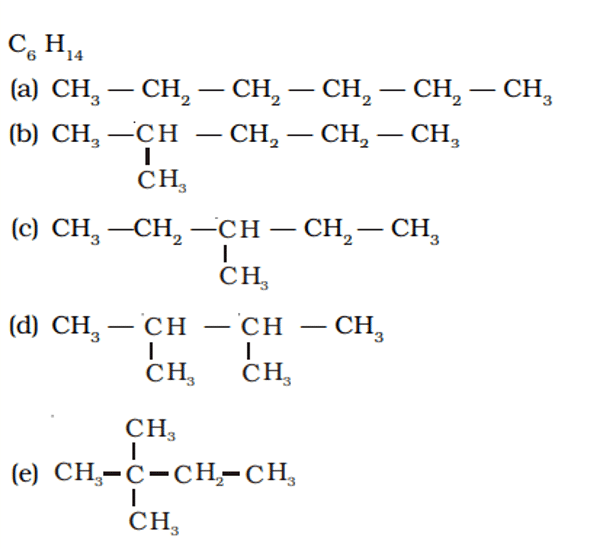
Q. No. 25) Draw structural formulae of all the possible isomers of the compound with molecular formula C3H6O and also give their electron dot structures.
Ans.
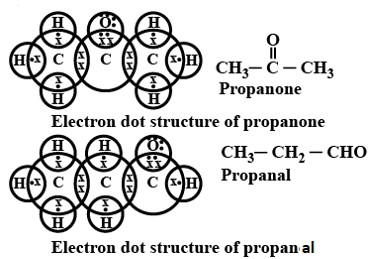
Q. No. 26) When ethanoic acid reacts with sodium hydrogen carbonate, a salt X is formed and a gas Y is evolved.
a. Identify X and Y. Write the chemical equation of the reaction involved.
b. Describe an activity and draw the diagram of the apparatus to prove that the evolved gas is the one that you have named.
Ans. a. CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2
X is Sodium ethanoate. Y is Carbon dioxide gas.
b.
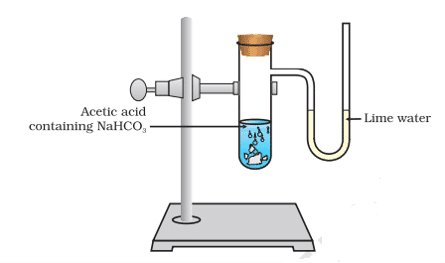
The gas evolved during the reaction is passed through a delivery tube into the test tube containing lime water. The lime water solution turns milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate, a characteristic property of CO2 gas.
Q. No. 27) Catenation is the ability of an atom to form bonds with other atoms of the same element. It is exhibited by both carbon and silicon. Compare the ability of catenation of the two elements. Give reasons.
Ans. Carbon exhibits catenation much more than silicon or any other element due to its smaller size which makes the C-C bonds strong while the Si-Si bonds are comparatively weaker due to their larger size.
Q. No. 28) (a) Write the formula and draw the electron dot structure of carbon tetrachloride.
(b) What is saponification? Write the reaction involved in this process.
Ans. (a) CCl4
b.

Saponification is the process of converting esters into salts of carboxylic acids and ethanol by treating them with a base.
Q. No. 29) What is the role of metal or reagents written on arrows in the given chemical reactions?
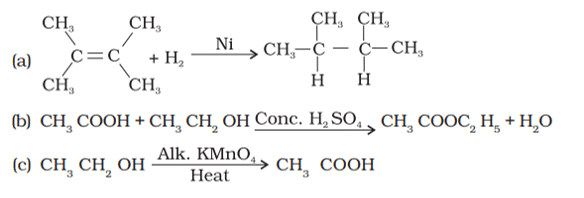
Ans. a. Ni acts as a catalyst.
b. Concentrated H2SO4 acts as a catalyst.
c. Alkaline KMnO4 acts as an oxidizing agent.
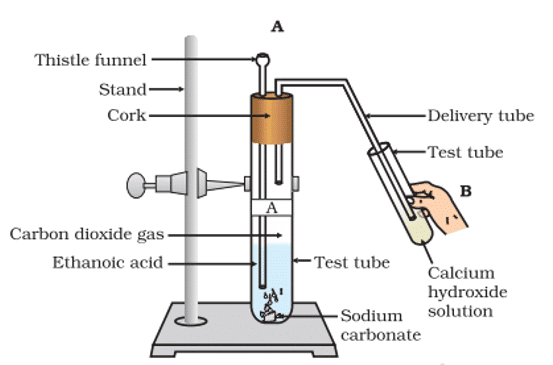
Q. No. 30) Look at the given figure and answer the following questions
a. What change would you observe in the calcium hydroxide solution taken in tube B?
b. Write the reaction involved in test tubes A and B respectively.
c. If ethanol is given instead of ethanoic acid, would you expect the same change?
d. How can a solution of lime water be prepared in the laboratory?
Ans. (a) It will turn milky.
(b) 2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COONa + H2O + CO2 (Test tube A)
Ca(OH)2 + CO2 → CaCO3 + H2O (Test tube B)
With excess CO2, milkiness disappears.
CaCO3 + H2O + CO2 → Ca(HCO3)2
(c) As C2H5OH and Na2CO3 do not react, a similar change is not expected.
C2H5OH + Na2CO3 → No change
(d) The lime water is prepared by dissolving calcium oxide in water and decanting the supernatant liquid.
Q. No. 31) How would you bring about the following conversions? Name the process and write the reaction involved.
a. Ethanol to ethene
b. Propanol to propanoic acid.
Write the reactions.
Ans. (a) By the dehydration of ethanol in the presence of concentrated H2SO4.
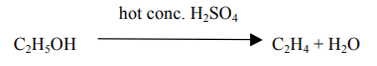
(b) By the oxidation of propanol using an oxidizing agent such as alkaline KMnO4.

Q. No. 32) The table given below shows the hints given by the quiz master in a quiz.
| S. No. | Hint |
| i. | Substance ‘C’ is used as a preservative. |
| ii. | ‘C’ has two carbon atoms; ‘C’ is obtained by the reaction of ‘A’ in presence of alkaline Potassium permanganate followed by acidification. |
| iii. | Misuse of ‘A’ in industries is prevented by adding Methanol, Benzene, and pyridine to ‘A’. |
| iv. | ‘F’ is formed on heating ‘A’ in presence of conc Sulphuric acid. |
| v. | ‘F’ reacts with Hydrogen gas in presence of Nickel and Palladium catalyst. |
Based on the above hints answer the following questions
a) Give the IUPAC names of A and F
b) Illustrate with the help of chemical equations the changes taking place. (A → C and A → F)
c) Name the chemical reactions which occur in steps 2 and 5. Identify the compounds formed in these steps if ‘A’ is replaced with its next homologue.
Ans. a. A - Ethanol; F - Ethene
b.


c. Oxidation, Addition/ Hydrogenation
Propanol, Propene
Q. No. 33) A carbon compound P has six carbon atoms and twelve hydrogen atoms.
(a) Is P a saturated or unsaturated carbon compound. Justify your answer by drawing the structural formula.
(b) Describe a test that can be used to determine if compound P is saturated or unsaturated.
(c) Name the products that are formed on burning compound P in an excess of air.
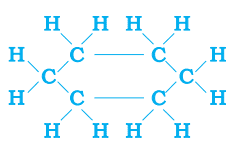
Ans. a. Compound P may be either saturated or unsaturated.
saturated compound: cyclohexane
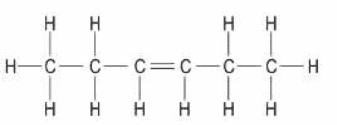
unsaturated compound: 2-hexene
b. Burning the compound in an excess of air will produce a sooty flame if it is unsaturated and a clean flame if it is saturated.
c. carbon dioxide and water
Q. No. 34) a. How are soaps different from detergents?
b. What makes water hard?
c. How is scum formed?
Ans. (a)
| Soap | Detergents |
| 1. Molecules of soap are sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids. | 1. Detergents are generally sodium salts of sulphonic acids or ammonium salts with chloride or bromide ions. |
| 2. Not so effective in hard water. | 2. It is effective even in hard water. |
| 3. It forms scum in hard water. | 3. Does not form scum in hard water. |
| 4. It has poor foaming capacity. | 4. It has a rich foaming capacity. |
| 5. Soaps are biodegradable. | 5. Most of the detergents are non-biodegradable. |
(b) The soluble salts of calcium and magnesium make the water hard.
(c) Scum is formed by the reaction of calcium or magnesium ions with soap molecules. These ions react with soap molecules forming calcium or magnesium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids which are insoluble and precipitate out.
Q. No. 35) What are the two properties of carbon that lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us?
Ans. The two properties of carbon that led to the huge number of carbon compounds are:
- Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon, giving rise to large molecules. This property is called catenation.
- Since carbon has a valency of four, it is capable of bonding with four other atoms of carbon or atoms of some other mono-valent element (Tetravalency).
Q. No. 36) Define homologous series of carbon compounds. Give an example of homologous series. List the characteristics of a homologous series.
Ans. A series of compounds in which the same functional group substitutes for hydrogen in a carbon chain is called a homologous series.
Example: CH3OH, C2H5OH, C3H7OH, C4H9OH, ….
Characteristics of homologous series:
- It has a general formula in terms of the number of carbon atoms.
- It has the same functional group.
- The members of a homologous series i.e., homologues, have similar chemical properties.
- The members of a homologous series i.e., homologues, show a gradation in physical properties with an increase in molecular mass.
- Formulae of two successive homologues differ by -CH2- unit.
- The difference in molecular mass between two successive homologues is 14 u.
Q. No. 37) Differentiate between ionic and covalent compounds.
Ans.
| Ionic compound | Covalent compound |
| 1. It is formed by the transfer of electrons. | 1. It is formed by sharing of electrons. |
| 2. It is formed between a metal and a non-metal. | 2. It is formed between two non-metals. |
| 3. It has high melting and boiling points. | 3. It has low melting and boiling points. |
| 4. Good conductor of electricity due to the formation of charged particles (ions). | 4. Bad/poor conductor of electricity due to the absence of charged particles (ions). |
Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds Class 10 NCERT Underlined PDF
| Must Read: Carbon and its Compounds Class 10 Notes to get an idea of the different types of questions asked from this chapter. |
| You Might Also Like: CBSE Class 10 Notes CBSE Class 10 Important Questions and Answers |
Hope you liked these Important Questions & Answers on Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds. Please share this with your friends and do comment if you have any doubts/suggestions to share.
Thank you very much sir 😊
My science sir are freshier and he don’t know many things from the syllabus and we can’t understand him but your video help me very much so thank you again
You are most welcome.
I have problem in Question No 9 in carbon ita compound how can I identify next homologue series
Just add -CH2- unit in the middle.
Add a -CH2 unit
Hey sir i am kiran sir only 5 days left in board our meri prepartion nai hou hai😓soo ( sir these question is enough for board? I want to score 80 per in exam
Thank you many many times sir . If we score good marks than there is only your hard work which you done for us 😊😊😊
You are most welcome..
Thank you very much Sir
In school teachers only say that this question came in this year but in what way they can’t explain so when I saw this i realised that how tricky questions will come from EQUATIONS
So nice
Thankyou so much sir
This helps me alot in preparation for my preboards…..
You are most welcome
Sir it’s a humble request on behalf of all 10 students
That please upload important questions of all chapters of science for aur betterment of upcoming exams.
Thank you sir🙏
Yes, I will try to upload as soon as possible
sir mereko ques 18 me doubt hai agar ham butanol ko heat karenge H2SO4 ke saath to C4H8 banna chaiye parr ‘P’ to C4H6 diya hua hai question me
Haa pahle C4H8 banta hai, fir kuch aur kaam karne par C4H6 banta hai. Ab C4H8 ko C4H6 banana aapke syllabus me nahi.
Sir ya sab question aa ya ga na board mai mako is saal bhi Dar lag raha h
Iss baat guarantee koi bhi nahi le sakta hai. Ye toh aap pe depend karega ki aap questions ko kaise prepare karte ho. Agar koi student ye sab questions prepare kar le toh uska preparation level kaafi acha ho jayega.
Dear Sir
Thank you very much for your word to word explanation and notes. It is really very helpful for self studing student like me.
Just would like to clarify one doubt regarding carbon and compounds syllabus. As per the syllabus it is written in cbse -enthanol properties and uses only, ethonic acid properties and uses only. what does it mean exactly ? is there any exclusion ?
Thanking you Sir
Sukruth.
“Properties and uses” means you have to study everything given in the NCERT textbook. There is no exclusion.
Sir 2023 borad
😁 Thank you so much sir for all your videos and notes. Your explanations and important questions have really made my basic concepts very strong and clear. You have made class 10th very easy for me. With genuine sincerity, thank you very much 🙏!
I hope to repay you back somehow in the future.
Best wishes for your future upcomings
too ! I wish you all the very best 👍!!
😁 Thank you so much sir for all your videos and notes. Your explanations and important questions have really made my basic concepts very strong and clear. You have made class 10th very easy for me. With genuine sincerity, thank you very much 🙏!
I hope to repay you back somehow in the future.
Best wishes for your future upcomings too! I wish you all the very best 👍!!
So nice of you! Keep watching and stay connected…
Qno 7 me doubt hai sir plz explain
Second member of CnH2n pucha hai. CnH2n Alkenes hote hai jiska series n=2 se start hota hai. So second member ke liye n=3 put karenge. Toh Propene milega answer me.
Ha sir smjh gye bahut bahut dhyavaad ….Term- 1 me mera chemestry me 10/26 aaya tha uss samay apke baare me pta nhi tha aur abhi recently carbon compound ka test me 22/24 aaya
Ab chemestry se dar nhi lgta….apki wajah se …..,😌😌
Sir 1 aur question tha ssc me jaise sample paper me diya hai usi pattern me uss particular chapter se question aayega na matlab agar political parties se 5no ka question diya hai sample paper me to utna marks ka hi aayega na……plz reply
So nice to see such a tremendous improvement in your performance.
Nahi aisa jaruri nahi hai ki same chapter se same marks ka question aayega. For eg. Political parties se 2 or 3 marks ka question bhi aa sakta hai. Chapterwise marks fix nahi hota hai. Subject-wise marks fix hai ki History-20 marks, Geometry-20 marks, Civics-20 marks, and Economics-20 marks ka aayega.
Q. No. 7) Write the name and formula of the 2nd member of the homologous series having the general formula CnH2n.
Ans. Propene, CH2=CH-CH3.
Sir ye samajh nahi aya sur second member to ethene, CH2=CH2. hoga na ?
CnH2n alkene hai. Alkene and Alkyne ka series n=2 se start hota hai. So first member ethene hoga and second member propene hoga.
A complete circuit is left on for several minutes, causing the connecting copper wire to become hot .As the temperature of the wire increases, the electrical resistance of the wire.
(A) decreases
(B) remains the same
(C) increases
(D) increases for some time and then decreases
Please explain me that
How the answer of this question is option (C)?
May be both are directly proportional
Sir, if I don’t do sample papers, can I get 90%? I have done all the questions on your website
No need to do sample papers now. I have included questions from sample papers in my questions. Just focus on revision.
A compound X is formed by the reaction of a Carboxylic acid C2H4O2 and an alcohol in presence of a few drops of H2So4. The alcohol on oxidation with alkaline KMnO4 followed by acidification give the same Carboxylic acid as used in this reaction give the names and structure of (a) Carboxylic acid (b) alcohol (c) the compound X also, write the reaction
Sir plz tell me the answer
It’s Really Fantastic 🤩 but more important questions we need
Sir are these questions enough for this chapter for boards??