If you're a Class 10 student preparing Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Control and Coordination, you may be wondering what types of questions to expect. To help you study and prepare, we've compiled a list of important questions and answers that cover key concepts and topics in this subject. With these resources, you'll be well-equipped to succeed on your exam and achieve your academic goals.

| Subject | Science (Chemistry) |
| Class | 10 |
| Board | CBSE & State Boards |
| Chapter No. | 6 |
| Chapter Name | Control and Coordination |
| Type | Important Questions & Answers |
| Session | 2024-25 |
"The future belongs to those who believe in the beauty of their dreams."
- Eleanor Roosevelt
Control and Coordination Class 10 Important Questions with Answers
Q. No. 1) Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
i. A gap between a pair of adjacent nerve cell over which nerve impulses passes is called _____.
a. Dendrites
b. Neurotransmitter
c. Synapse
d. All of these
Ans. Option (c).
ii. The electrical impulse travels in a neuron from
a. Dendrite → axon → axonal end → cell body
b. Cell body → dendrite → axon → axonal end
c. Dendrite → cell body → axon → axonal end
d. Axonal end → axon → cell body → dendrite
Ans. Option (c).
iii. Which of the following statements about the transmission of nerve impulses is incorrect?
a. Nerve impulse travels from the dendritic end towards the axonal end.
b. At the dendritic end electrical impulses bring about the release of some chemicals which generate an electrical impulse at the axonal end of another neuron.
c. The chemicals released from the axonal end of one neuron cross the synapse and generate a similar electrical impulse in a dendrite of another neuron.
d. A neuron transmits electrical impulses not only to another neuron but also to muscle and gland cells.
Ans. Option (b).
iv. Which of the following statements is true?
- Sudden action in response to something in the environment is called reflex action.
- Sensory neurons carry signals from the spinal cord to muscles.
- Motor neurons carry signals from receptors to the spinal cord.
- The path through which signals are transmitted from a receptor to a muscle or a gland is called the reflex arc.
Options
a. 1 and 2
b. 1 and 3
c. 1 and 4
d. 1, 2, and 3
Ans. Option (c).
v. Which is the correct sequence of the components of a reflex arc?
a. Receptors → Muscles → Sensory neuron → Motor neuron → Spinal cord
b. Receptors → Motor neuron → Spinal cord → Sensory neuron → Muscle
c. Receptors → Spinal cord → Sensory neuron → Motor neuron → Muscle
d. Receptors → Sensory neuron → Spinal cord → Motor neuron → Muscle
Ans. Option (d).
vi. Which is the largest part of the brain?
a. Medulla Oblongata
b. Pons
c. Cerebellum
d. Cerebrum
Ans. Option (d).
vii. Which of the following statements are true about the brain?
- The main thinking part of the brain is the hindbrain.
- Centers of hearing, smell, memory, sight, etc. are located in the forebrain.
- Involuntary actions like salivation, vomiting, and blood pressure are controlled by the medulla in the hindbrain.
- Cerebellum does not control the posture and balance of the body.
Options
a. 1 and 2
b. 1, 2, and 3
c. 2 and 3
d. 3 and 4
Ans. Option (c).
viii. Precision in voluntary action is due to:
a. Pons
b. Medulla oblongata
c. Cerebrum
d. Cerebellum
Ans. Option (d).
ix. Observe the figure given below.
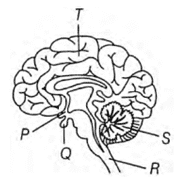
In the figure, some parts are labeled as P, Q, R, S, and T. Given below are functions associated with these parts.
| Parts of brain | Functions |
| P | Master hormone producer |
| Q | Controls body temperature |
| R | Controls unconscious activities |
| S | Helps to control the balance |
| T | In conscious behavior |
Which part of the brain is matched with incorrect function?
a. P and S
b. P, Q, and T
c. R and T
d. P, R, and T
Ans. Option (b).
Part P (hypothalamus) controls body temperature.
Part Q (pituitary) is the master hormone producer.
Part T (cerebrum) helps in memory storage and conscious behavior.
x. Posture and balance of the body are controlled by _____.
a. Cerebrum
b. Cerebellum
c. Medulla
d. Pons
Ans. Option (b).
xi. The growth of tendrils in pea plants is due to
a. Effect of light
b. Effect of gravity
c. Rapid cell divisions in tendrillar cells that are away from the support
d. Rapid cell divisions in tendrillar cells in contact with the support
Ans. Option (c).
xii. Which one of the following is not a tropic movement?
a. Movement of shoot towards light
b. Movement of roots toward water
c. Movement of roots toward gravity
d. Drooping of leaves of Mimosa pudica on touching
Ans. Option (d).
xiii. Select the mismatched pair:
a. Adrenaline – Pituitary gland
b. Testosterone – Testes
c. Estrogen – Ovary
d. Thyroxin – Thyroid gland
Ans. Option (a).
xiv. A deficiency of iodine will cause this disease in the body:
a. Beri Beri
b. Goitre
c. Marasmus
d. Night Blindness
Ans. Option (b).
xv. Identify which of the following statements is incorrect about thyroxin?
a. Thyroid gland requires iodine to synthesize thyroxin
b. Iron is essential for the synthesis of thyroxin
c. It regulates protein, carbohydrates, and fat metabolism in the body
d. Thyroxin is also called the thyroid hormone
Ans. Option (b).
xvi. Person X suffers from a condition that affects the normal functioning of the pituitary gland.
Which of the following is most likely a direct effect of person X’s condition?
a. Insufficiency of iodine
b. Irregular heartbeat
c. Insufficient growth of the body
d. Inability to regulate blood sugar
Ans. Option (c)
xvii. The hormone which is responsible for the maintenance of sugar levels in the blood:
a. Growth hormone
b. Gibberellin
c. Insulin
d. Estrogen
Ans. Option (c).
xviii. The changes associated with puberty are because of the secretions secreted by:
a. Pancreas
b. Adrenal gland
c. Thyroid gland
d. Gonads
Ans. Option (d). (Gonad: an organ that produces gametes; a testis or ovary)
xix. Assertion (A): The timing and amount of hormone released are regulated by feedback mechanisms.
Reason (R): Oversecretion and under-secretion of hormones are harmful to the body.
Options
a. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
b. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
c. A is true but R is false.
d. A is false but R is true.
Ans. Option (b).
Q. No. 2) Read the functions of the following plant hormones and name them:
a. Promote cell enlargement and cell differentiation and promote fruit growth.
b. Promote cell enlargement and cell differentiation in the presence of auxins and help in breaking the dormancy in seeds and buds.
c. Promote cell division, promote the opening of stomata and also fruit growth, help in breaking the dormancy of seeds and buds, and delay the aging in leaves.
d. Promote the dormancy in seeds and buds, promote the closing of stomata and falling of leaves.
Ans. a. Auxins
b. Gibberellins
c. Cytokinin
d. Abscisic acid
Q. No. 3) Match the following
i.
| Column I | Column II |
| a. Cerebrum | p. controls the pituitary |
| b. Cerebellum | q. controls vision and hearing |
| c. Hypothalamus | r. controls the rate of heartbeat |
| d. Midbrain | s. seat of intelligence |
| t. maintains body posture |
Ans. a-s, b-t, c-p, d-q.
ii.
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Dendrite | a. the impulse is converted into a chemical signal for onward transmission. |
| 2. Axon | b. blood pressure and vomiting |
| 3. Nerve endings | c. where information is acquired |
| 4. Forebrain | d. walking in a straight line |
| 5. Cerebellum | e. through which information travels as an electrical impulse |
| 6. Medulla | f. hearing and sight |
Ans. 1-c, 2-e, 3-a, 4-f, 5-d, 6-b.
iii.
| Column I | Column II |
| a. Olfactory receptors | i. Tongue |
| b. Thermo receptors (temperature receptors) | ii. Eye |
| c. Gustatoreceptors | iii. Nose |
| d. Photoreceptors | iv. Skin |
Ans. a-iii, b-iv, c-i, d-ii
Q. No. 4) Draw a neat diagram of a neuron and label the following:
a. Part where information is first received.
b. Part through which it travels.
c. Part through which it is released.
Ans.
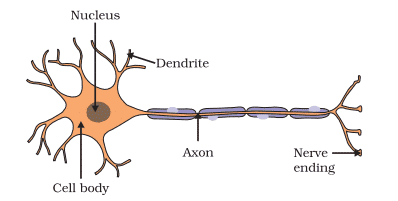
a. Dendrite
b. Axon
c. Axon terminal/Nerve ending.
Q. No. 5) Why is the flow of signals in a synapse from the axonal end of one neuron to the dendritic end of another neuron but not the reverse?
Ans. When an electrical signal reaches the axonal end of a neuron, it releases a chemical substance. This chemical diffuses towards the dendrite end of the next neuron where it generates an electrical impulse or signal. Hence, the electrical signal is converted into a chemical signal at the axonal end. Since these chemicals are absent at the dendrite end of the neuron, the electrical signal cannot be converted into a chemical signal.
Q. No. 6) Draw a well-labeled diagram of a reflex arc and show the direction of the flow of electrical signals.
Ans.
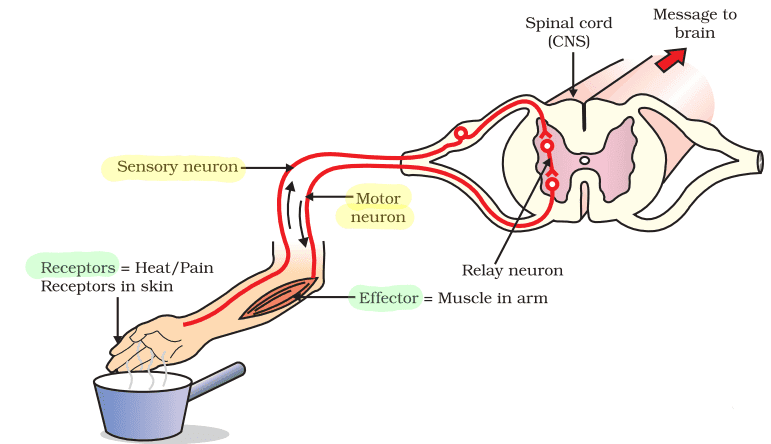
Sense Organ -----(Sensory neuron)→ Spinal Cord (CNS) ----(Motor neuron)→ Effector (Muscle in arm).
Q. No. 7) i. Draw a neat diagram of the human brain and label the medulla and cerebellum.
ii. Write the functions of the above-mentioned parts.
Ans. i.
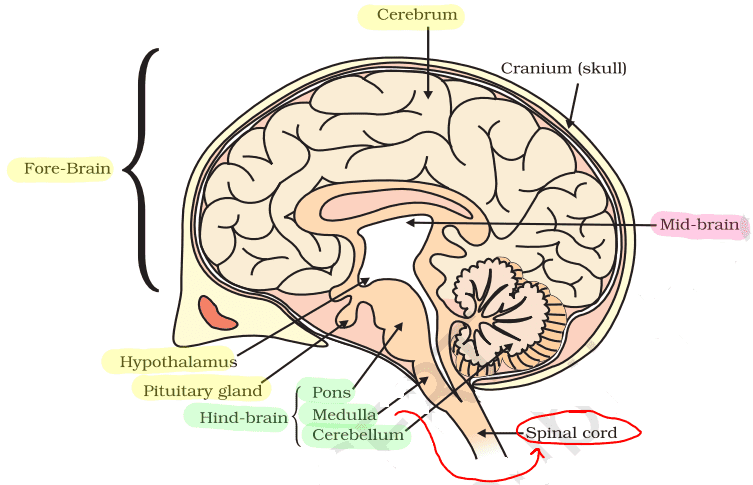
ii. Medulla controls blood pressure, salivation, and vomiting.
The cerebellum controls the precision of voluntary movements and equilibrium.
Q. No. 8) How are the brain and spinal cord protected in the human body?
Ans. The brain is covered with a cranium and the spinal cord is protected by the vertical column or backbone. These bony covers protect both from external injuries. Both the brain and spinal cord are covered with three membranes called meninges. The space between meninges is filled with a fluid called cerebrospinal fluid which protects them from mechanical shock.
Q. No. 9) How is the mode of action in the beating of the heart different from reflex actions? Give four examples.
Ans.
| Beating of heart | Reflex action |
| i. Involuntary actions are actions that are not controlled by our will. | i. Reflex actions are sudden actions in response to something. |
| ii. They do not need any kind of stimulus to work. | ii. They require stimulus for action. |
| iii. These actions are regulated by the brain. | iii. These actions are regulated by the spinal cord. |
| iv. They do not involve skeletal muscle. | iv. They do involve skeletal muscle. |
| v. These actions are performed throughout one's life. | v. These actions are produced in response to an event of an emergency. |
| vi. This action may be quick or slow. | vi. Reflex actions are always quick. |
Q. No. 10) What are tropic movements? Describe different types of tropic movements.
Ans. The movements which are in a particular direction in relation to the stimulus are called tropic movements. Tropic movements happen as a result of the growth of a plant part in a particular direction. There are four types of tropic movements, viz. Phototropic, Geotropic, Hydrotropic, and Thigmotropic.
- Phototropic movement: The growth in a plant part in response to light is called phototropic movement. Stems usually show positive phototropic movement, while roots usually show negative phototropic movement.
- Geotropic movement: The growth in a plant part in response to gravity is called geotropic movement. Roots usually show positive geotropic movement, i.e., they grow in the direction of gravity. Stems usually show negative geotropic movement.
- Hydrotropic movement: When roots grow in the soil, they usually grow toward the nearest source of water. This shows a positive hydrotropic movement.
- Thigmotropic movement: The growth in a plant part in response to touch is called thigmotropic movement. Such movements are seen in the tendrils of climbers. The tendril grows in a way so that it can coil around support. The differential rate of cell division in different parts of the tendril happens due to the action of auxin.
Q. No. 11) a. How is the movement in “touch me not plant” different from that of shoot towards light?
b. Describe positive and negative geotropism through an experiment.
Ans. a.
| Movement of shoot towards the light (Phototropism) | Movement in "Touch me not" plant (Nastic movement) |
| i. It is a slow response toward any stimulus. | i. It is an immediate response to a stimulus. |
| ii. It is directional. | ii. It is non-directional. |
| iii. It is growth dependent. | iii. It is growth independent. |
b. Set up: i. Take a potted plant and keep it in sunlight in a horizontal position.
ii. Observe the growth of the shoot and root of the plant.
Observation: i. The roots bend downward showing positive geotropism.
ii. The shoot bends upwards towards sunlight showing negative geotropism.
Q. No. 12) In the figures given below, which appears more accurate and why?
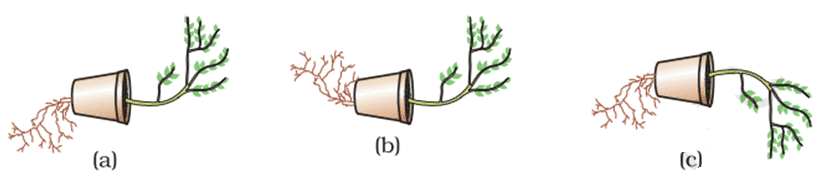
Ans. Figure (a) is more appropriate because in a plant shoots are negatively geotropic hence, grow upwards and roots are positively geotropic so grow downwards.
Q. No. 13) Explain giving reasons for the bending of the shoot tip of a plant towards a light source coming from one side of the plant.
Ans. When growing plants detect light, a hormone called auxin, synthesized at the shoot tip, helps the cells to grow longer. When light is coming from one side of the plant, auxin diffuses towards the shady side of the shoot. This concentration of auxin stimulates the cells to grow longer on the side of the shoot which is away from light. Thus, the plant appears to bend towards the light.
Q. No. 14) Give reasons:
a. Pituitary is often termed as a master endocrine gland.
b. Pancreas helps in digestion and also regulates blood sugar levels.
c. Adrenals are known as glands of emergency.
Ans. a. Pituitary is often called a master endocrine gland because it controls and coordinates the secretion of all the other endocrine glands.
b. Pancreas secretes pancreatic juice as well as a hormone called insulin. Pancreatic juice helps in digestion whereas insulin regulates blood sugar levels.
c. Emergency hormone in our body is adrenaline. It helps in coping during emergencies as it is secreted directly into the blood and carried to different parts of the body as a result the heart beats faster, resulting in a supply of more oxygen to our muscles. The blood to the digestive system and skin is reduced due to the contraction of muscles around small arteries in these organs. This diverts the blood to our skeletal muscles. The breathing rate also increases because of the contraction of the diaphragm and rib muscles. All these responses together enable the animal body to be ready to deal with the emergency situation.
Q. No. 15) Nervous and hormonal systems together perform the function of control and coordination in human beings. Justify the statement.
Ans. The nervous and hormonal systems together perform the function of control and coordination in human beings. For example: in the case of any emergency, the stimulus is perceived by the central nervous system. The stimulus is analyzed and the response is sent to the effectors. Simultaneously, sympathetic nerves stimulate the adrenal gland to release adrenaline which regulates blood pressure, increases heartbeat, constricts blood vessels, dilates the pupil, etc. In this way, both nervous and endocrine systems interact and overcome the crisis together.
Q. No. 16) How do control and coordination in plants differ from that in animals?
Ans.
| Control in plants | Control in animals |
| i. Plant hormones diffuse to the place of action. | i. Animal hormones are carried in blood vessels. |
| ii. Plants depend on hormones for control and coordination. | ii. Animals depend on nerve impulses and hormones for control and coordination. |
| iii. Hormones in plants are not secreted by specialized glands. | iii. Hormones in animals are secreted by specialized glands. |
| iv. Movement in plants occurs through a change in the water content of the action cells. | iv. Movement in animals occurs through a change in the shape and arrangement of proteins in the muscle cells. |
Q. No. 17) Label the endocrine glands in the figure given below.
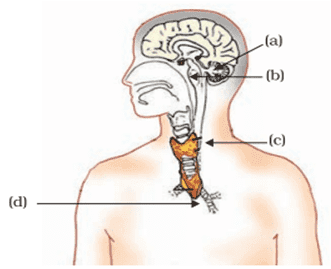
Ans. a. Pineal gland
b. Pituitary gland
c. Thyroid gland
d. Thymus
Q. No. 18) Pertaining to the endocrine system, what will you interpret if-
i. You observe swollen necks in people living in the hills
ii. Over-secretion of growth hormone takes place during childhood
iii. Facial hair develops in boys aged 13.
Ans. i. Less intake of iodine in the diet.
ii. Will lead to gigantism.
iii. Timely secretion of testosterone.
Q. No. 19) “Both overproduction and underproduction of the Growth hormone lead to disorders in the body.” Explain.
Ans. The overproduction of growth hormone leads to gigantism and its underproduction leads to dwarfism.
Q. No. 20) Answer the following:
a. Name the endocrine gland associated with the brain.
b. Which gland secretes digestive enzymes as well as hormones?
c. Name the endocrine gland associated with kidneys.
d. Which endocrine gland is present in males but not in females?
Ans. a. Pituitary
b. Pancreas
c. Adrenal
d. Testes
| Must Read: Control and Coordination Class 10 Notes to get an idea of the different types of questions asked from this chapter. |
| You Might Also Like: CBSE Class 10 Notes CBSE Class 10 Important Questions and Answers |
Hope you liked these important questions and answers on Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Control and Coordination. Please share this with your friends and do comment if you have any doubts/suggestions to share.
Sir iske baad v NCERT Examplar ke questions karne hai kya?
Naa jarurat nahi hai. Kam padho aur usko revise karo.
Sir, kya mai in sare chapter ke imp questions pad kar exam mai top kar
sakti hoon
Haa
Kr liya top aapny? Ja 23-24 ka batch hai??
Sir, you are the best ,,thank you very much.
Glad you think so
Thank you sir ,, you are the best
Most welcome 🤗
Sir in 3 question midbrain changes size of pupil but fore brain helps in hearing , sight and so on . Sir I have a doubt that are these important questions only sufficient for boards 2023-2024 . Please reply
nice questions with meaning ful explanations will really help the needy.
Bhai iski PDF download kase krni h mare se download nhi ho rhi important questions wali
How to Download PDF from CBSE Guidance Website
https://youtu.be/zjocgf0LzUM