Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Class 10 Science Chapter 12: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current. As the CBSE 2023-24 board exams approach, it's crucial to delve into this fundamental chapter, exploring its intricate concepts and applications. In this Q&A blog post, we'll navigate through essential questions and provide detailed answers that align with the latest syllabus. Whether you're seeking a better understanding of electromagnetism or preparing for exams, we've compiled a PDF of important questions and answers to assist you in mastering this intriguing subject. Join us as we unravel the mysteries of magnetic effects intertwined with electric currents, ensuring you're well-equipped for academic success in your Class 10 Science examinations.
| Subject | Science (Physics) |
| Class | 10 |
| Board | CBSE & State Boards |
| Chapter No. | 12 |
| Chapter Name | Magnetic Effect of Electric Current |
| Type | Important Questions & Answers |
| Session | 2023-24 |
"The secret of getting ahead is getting started."
- Mark Twain
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Class 10 Questions & Answers
Q. No. 1) Fill in the blanks:
a. In a magnetic field pointing away from you, an electron traveling to the right will experience a force in the ______ direction.
b. In our houses we receive AC electric power of ______ with a frequency of ______.
c. In a magnetic field pointing away from you, an electron traveling to the right will experience a force in the ________ direction.
d. No force acts on a current-carrying conductor when it is ________ to the magnetic field.
Ans. a. Downward
b. 220 V, 50 Hz.
c. downward
d. parallel
Q. No. 2) Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
i. Choose the incorrect statement from the following regarding magnetic lines of field:
a. The direction of the magnetic field at a point is taken to be the direction in which the north pole of a magnetic compass needle points.
b. Magnetic field lines are closed curves.
c. If magnetic field lines are parallel and equidistant, they represent zero field strength.
d. Relative strength of the magnetic field is shown by the degree of closeness of the field lines.
Ans. Option (c).
ii. If the key in the arrangement is taken out (the circuit is made open) and magnetic field lines are drawn over the horizontal plane ABCD, the lines are
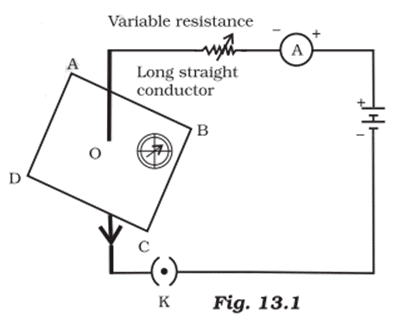
a. Concentric circles
b. Elliptical in shape
c. Straight lines parallel to each other
d. Concentric circles near point O but of elliptical shapes as we go away from it.
Ans. Option (c).
iii. For a current in a long straight solenoid N- and S-poles are created at the two ends. Among the following statements, the incorrect statement is:
a. The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of straight lines which indicates that the magnetic field is the same at all points inside the solenoid.
b. The strong magnetic field produced inside the solenoid can be used to magnetize a piece of a magnetic material like soft iron when placed inside the coil.
c. The pattern of the magnetic field associated with the solenoid is different from the pattern of the magnetic field around a bar magnet.
d. The N- and S-poles exchange position when the direction of current through the solenoid is reversed.
Ans. Option (c).
iv. A positively charged particle (alpha-particle) projected towards the west is deflected towards the north by a magnetic field. The direction of the magnetic field is:
a. Towards south
b. Towards east
c. Downward
d. Upward
Ans. Option (d).
v. The most important safety method used for protecting home appliances from short-circuiting or overloading is:
a. Earthing
b. Use of fuse
c. Use of stabilizers
d. Use of an electric meter
Ans. (b) Use of fuse.
vi. The frequency of AC in some countries is 60 Hz.
What does this mean?
a. The current changes direction 60 times in a second
b. The current changes direction 120 times in a second
c. The current changes direction after every 60 seconds
d. The current changes direction after every 120 seconds
Ans. Option (b) [In India, the AC changes direction after every 1/100 second, that is, the frequency of AC is 50 Hz]
vii. Which circuit shows the correct and safe positions for the fuse and the switch?
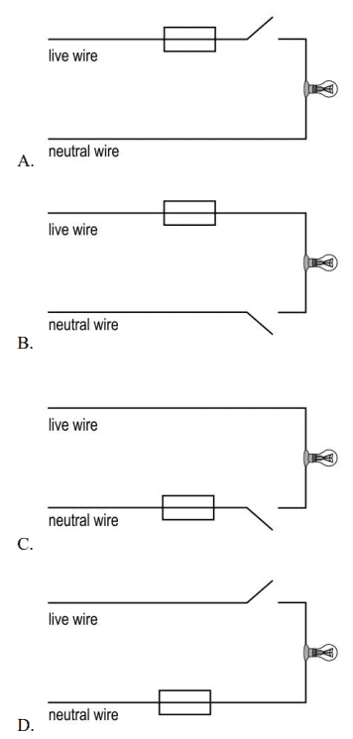
Ans. Option (a)
viii.
- Assertion (A): A stationary charged particle placed in a magnetic field experiences a force.
- Reason (R): A stationary charged particle does not produce a magnetic field.
Options
a. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b. Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
c. A is true but R is false
d. A is false but R is true
Ans. Option (d)
Q. No. 3) Give two uses of a magnetic compass.
Ans.
- In navigation, it is used to find directions.
- It is used to detect a magnetic field.
- It can be used to test whether a substance is magnetic or not.
Q. No. 4) Define the term magnetic field. What are magnetic field lines? Mention the properties of magnetic field lines.
Ans. Magnetic field: The region surrounding a magnet, in which the force of the magnet can be detected is called its magnetic field.
Field lines: Field lines are used to represent a magnetic field. A field line is a path along which a hypothetical free north pole would tend to move.
Properties of field lines:
- The magnetic field is a quantity that has both direction and magnitude.
- It is taken by convention that the field lines emerge from the north pole and merge at the south pole. Inside the magnet, the direction of field lines is from its south pole to its north pole. Thus the magnetic field lines are closed curves.
- The relative strength of the magnetic field is shown by the degree of closeness of the field lines. The closer the field lines, the stronger the strength of the magnetic field.
- No two field lines cross each other. (If they cross, it would mean that at the point of intersection, the magnetic compass needle would point toward two directions, which is not possible.
Q. No. 5) Why two magnetic field lines cannot intersect each other?
Ans. If two magnetic field lines intersect each other, it would mean that at the point of intersection, the compass needle would point toward two directions, which is not possible.
Q. No. 6) Draw the patterns of magnetic field lines due to a bar magnet. The magnetic field lines are closed curves. Why?
Ans.
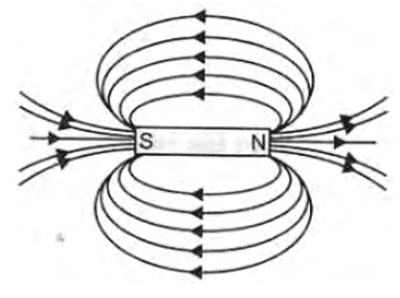
Magnetic field lines emerge from the N-pole of a bar magnet and go to the S-pole and inside the magnet field lines go from S-pole to N-pole. Thus they form closed curves.
Q. No. 7) Identify the poles of the magnet in the given figures:
i.
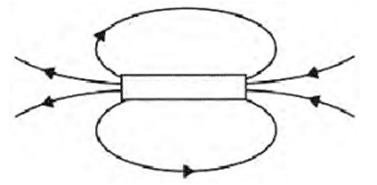
ii.
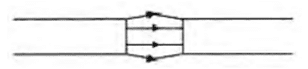
Ans.
i.
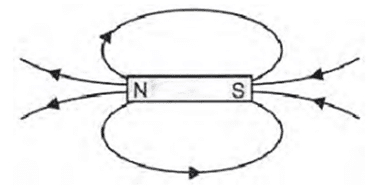
ii.
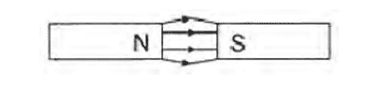
Q. No. 8) How will you find out the direction of a magnetic field produced by a current-carrying conductor?
Ans. The direction of the magnetic field produced by the current-carrying conductor can be found by applying the Right-Hand Thumb Rule. According to this rule, if we are holding a current-carrying straight conductor in our right hand such that the thumb points towards the direction of the current, then our fingers will wrap around the conductor in the direction of the field lines of the magnetic field.
Q. No. 9) P and Q represent two straight wires carrying equal current (I) in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the screen outwards. K is the midpoint of the line joining P and Q. The image shows the magnetic field lines around the wire. But the direction of the magnetic field is not marked.
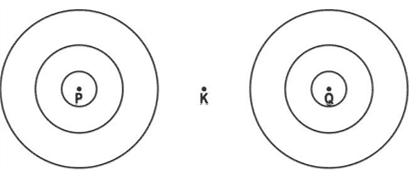
i. Draw the above image and mark the direction of the magnetic field.
ii. If the current in the wires is increased, how will the strength of the magnetic field around P and Q change? Draw the magnetic field lines around P and Q to represent this change.
iii. If B is the magnetic field at point K due to the current in wire P, what will be the magnetic field due to P and Q at the midpoint K? Give a reason for your answer.
iv. If B is the magnetic field at point K due to the current in wire P and the current in wire Q is reversed, what will be the magnetic field at midpoint K?
Ans. i. Using Right-Hand Thumb Rule,
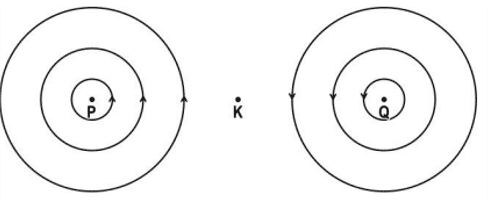
ii. The strength of the magnetic field around P and Q will increase.
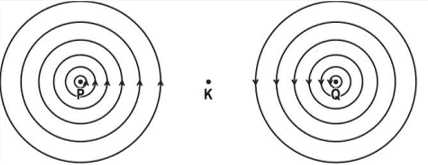
iii. Zero, because the magnetic fields at point K due to current in the wires P and Q are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction. The two fields cancel each other.
iv. 2B
Q. No. 10) Define a solenoid. With the help of a suitable diagram show the pattern of magnetic field lines around a current-carrying solenoid. State the region where the field is uniform.
Ans. Solenoid: A coil of many circular turns of insulated copper wire wrapped closely in the shape of a cylinder is called a solenoid.
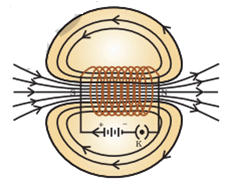
The magnetic field is uniform inside the solenoid.
Q. No. 11) A helical coil whose length is greater than its diameter is connected to a battery as shown below.
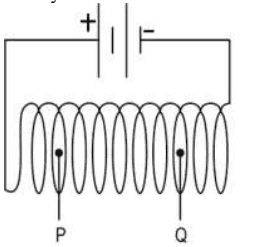
(a) How does the magnetic field at point P compare with the magnetic field at point Q? Justify your answer.
(b) State one way in which the strength of the magnetic field inside a current-carrying helical coil can be changed.
Ans. a. The magnetic field at P and Q is the same.
Because the magnetic field lines inside the helical coil of wire which behaves like a solenoid is uniform/in the form of parallel straight lines.
b.
- increasing/decreasing the number of turn in the coil
- increasing/decreasing the current through the coil
Q. No. 12) Explain factors on which the strength of the magnetic field produced by a current-carrying solenoid depends.
Ans. The strength of a magnetic field is directly proportional to:
- The number of turns in the solenoid.
- The current in the solenoid.
Q. No. 13) List factors affecting the strength of the magnetic produced by a straight conductor carrying current.
Ans.
- The strength of a field is directly proportional to the current passing through the conductor.
- The strength of the field is inversely proportional to the perpendicular distance from the conductor.
Q. No. 14) a. Describe an experiment with a diagram to show that force is exerted on a current-carrying conductor when placed perpendicular to a magnetic field.
b. How will the force change if the current in the conductor is increased?
Ans. a.
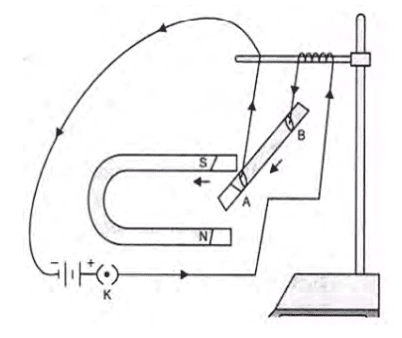
Take a small metal rod AB and suspend it from a stand with the help of two connected wires. Put the in between the horseshoe magnet in such a way that the rod remains in between the two poles. Pass the current in the rod through the two wires. You would find that the rod is deflected towards the left. Now reverse the direction of the current, and the rod is deflected in opposite direction. This show that a force is experienced by a current-carrying conductor in the magnetic field.
b. If the current in the conductor is increased then more force will act on the rod, and get more deflected.
Q. No. 15) When is the force exerted on a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field maximum and when is it minimum?
Ans. i. The magnitude of the force is the highest/maximum when the direction of the current is at right angles/perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field.
ii. The magnitude of the force is minimum when the direction of the current is parallel to the direction of the magnetic field.
Q. No. 16) A current through a horizontal power line flows in the west-to-east direction.
i. What is the direction of the magnetic field at a point directly above it and a point directly below it?
ii. Name the rule used to determine
a. The direction of force when a current-carrying wire is placed in a strong magnetic field.
b. Magnetic field in a current-carrying conductor.
iii. Is there a similar magnetic field produced around a thin beam of moving:
a. Alpha particles
b. Neutrons
Justify your answer.
Ans. i. The current is in the west-to-east direction. Applying the right-hand thumb rule, we get the direction of the magnetic field at a point above the wire from the North-South direction. The direction of the magnetic field at a point directly below the wire is from the South-North direction.
ii. a. Fleming’s left-hand rule.
b. Right-hand thumb rule.
iii. a. Yes, Alpha particles being positively charged constitutes a current in the direction of motion.
b. No, a neutron being electrically neutral constitutes no current.
Q. No. 17) An electron enters a uniform magnetic field at right angles to it as shown in the figure below. In which direction will this electron move? State the rule applied by you in finding the direction of motion of the electron.
Ans. As per Fleming’s left-hand rule, the electron will experience a force upward.
Fleming’s left-hand rule: Stretch the forefinger, the middle finger, and the thumb of the left hand mutually perpendicular to each other in such a way that the forefinger points the direction of the magnetic field, the middle finger points the direction of current (opposite to the direction of flow of electrons) then the thumb will point the direction of the force on the conductor.
Q. No. 18) Distinguish between a direct current and an alternating current.
Ans.
| Direct Current (dc) | Alternating Current (ac) |
| i. It is the current of constant magnitude. | i. It is the current of magnitude varying with time. |
| ii. It flows in one direction in the circuit. | ii. It reverses its direction while flowing in a circuit. |
| iii. It is obtained from a cell or battery. | iii. It is obtained from a.c. generator and mains. |
Q. No. 19) a. Name the type of electric current generated by most of the power stations in our country.
b. Why is it preferred over the other type?
c. State the frequency of the power supply generated in India.
Ans. a. Alternating current.
b. AC can be transmitted over long distances without much loss of energy.
c. 50 Hz.
Q. No. 20) a. What is the standard color code followed for:
i. Live
ii. Neutral, and
iii. Earth wire used in electric circuits?
b. Which part of an electric appliance is earthed and why?
Ans. a. The standard color code for
i. Live wire – Red
ii. Neutral – Black
iii. Earth – Green
b. The metallic case of an electrical appliance is earthed because metals are good conductors of electricity and in case if current exceeds i.e., live wire touches the metallic case of an appliance, then due to earthing all the excess amount of current flows down to the earth and we prevent ourselves from an electric shock.
Q. No. 21) Sunita had to replace the electrical plug of her clothes iron. She bought a three-pin plug as shown below.
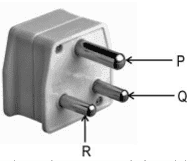
When she removed the old plug, she saw that there were three wires colored red, black, and green.
i. To which pin on the plug should she connect the green wire?
ii. To which part of the clothes iron is the green wire connected?
iii. State the function of the green wire.
Ans. i. Pin P.
ii. To the metallic body of the clothes iron.
iii. It prevents severe shocks by providing a low resistance path for any leakage current to the metallic body of the iron
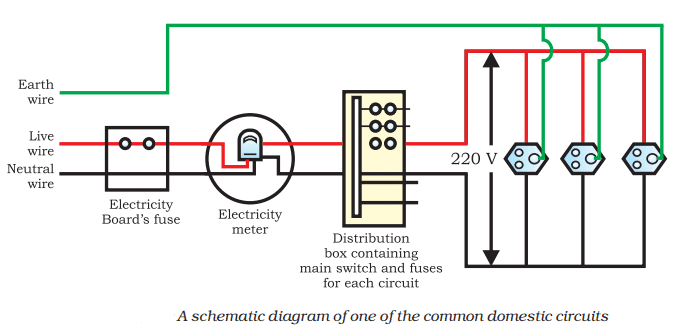
Q. No. 22) Draw a schematic labeled diagram of a domestic wiring circuit which includes
i. The main fuse
ii. A power meter
iii. One light point, and
iv. A power plug.
Ans.
Q. No. 23) a. What do you understand by a short circuit?
b. What is overloading? How can you avoid overloading?
Ans. a. Short circuiting means when live wire and the neutral wires come in contact with each other, the resistance of the circuit becomes very small, and a huge amount of current flows through the circuit which in turn produces more heat which can cause a fire.
b. Overloading means a large amount of current flows in the circuit. It can happen when many electrical appliances of high power ratings are connected in a single socket.
Overloading can be avoided by the following methods:
- Do not use too many appliances in a single socket.
- Ensure that wires are properly insulated.
- Ensure that the appliances/devices are not faulty.
Q. No. 24) What is the function of an electric fuse?
Ans. It is a safety device that protects the circuit in case excess current flows through the circuit. When a high current flows through a circuit, the fuse wire gets heated and melts. This breaks the circuit and the current stops flowing.
Q. No. 25) Evaluate the need of connecting an electric fuse in an electric circuit. Also judge if an electrician puts a fuse of rating 15A in that part of a domestic electric circuit in which an electric heater of rating 1.5 kW, 220 V is operating. What is likely to happen in this case and why? What change, if any, needs to be made?
Ans. An electric fuse connected to the live wire in an electric circuit prevents damage to the appliances and the circuit due to overloading or short-circuiting. If an electric current is more than the rating of fuse flows in a circuit, the fuse wire melts, and the circuit breaks.
Electric current (I) in the above circuit:
I = P/V = 1.5x1000/220 = 1500/220 = 6.82 A
The current flowing in the circuit is 6.82 A which is much less than the fuse rating which is 15 A. Therefore the fuse will not melt even in case of overloading or short-circuiting and the electrical fuse is not serving its purpose. To operate the heater, a fuse of lower rating 7 A is to be put in the circuit.
Q. No. 26) An air conditioner of 2 kW is used in an electric circuit having a fuse of 10 A rating. If the potential difference of the supply is 220 V, will the fuse be able to withstand, when the air conditioner is switched on? Justify your answer.
Ans. Given: P = 2 kW = 2000 W
V = 220 V
Therefore, I = P/V = 2000/220 = 9.09 A
The rating of the fuse is 10 A which is greater than current drawn by the air conditioner. So when the air conditioner is switched on, the fuse will not blow off.
Q. No. 27) Find the minimum rating of fuse that can be safely used on a line on which two 1.1 kW electric geysers are to run simultaneously. The supply voltage is 220 V.
Ans. Given: P = 2 x 1.1 kW = 2 x 1.1 x 1000 W = 2200 W
V = 220 V
Therefore, I = P/V = 2200/220 = 10 A
So, a fuse wire rating must be greater than 10 A.
Download Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Class 10 (Chapter 12) Class 10 NCERT Underlined PDF
| Must Read: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Class 10 Notes to get an idea of important concepts in this chapter. |
| You Might Also Like: CBSE Class 10 Notes CBSE Class 10 Important Questions and Answers |
Hope you liked these Important/Extra Questions & Answers on Class 10 Science Chapter 12 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current. Please share this with your friends and do comment if you have any doubts/suggestions to share.

Thank you so much for uploading these fantastic questions related to this chapter
Waiting for next chapters 🙏🙃
You are always welcome. I am working on other chapters. You will get them soon.
Tq very this site is very useful..
Thanks sir 🙏🙏🙏
This site is very useful for 11th hour revision
Sir plz upload electricity chapter important questions answers
Yes it is coming on this Saturday.
Sir please send important question on electricity
Yes working on it. Will be uploaded by this week end.
Plz sir upload electricity chapter important questions answers
Thanku sir 😃
You are the best teacher in the world thanks for this wonderful help
Glad you liked it. 🤗
Sir thanku so much for real ❤️you deserve much more ..you are very hardworking and I m not able to express my gratitude in words ..thanku so much ❤️ you are much and more better than all of the other teachers on YouTube ❣️
Sir ek problem ha….human eye ka important questions ka part pata nahi kyu open hi nahi ho raha…click karnese apka website ka actual page me phirse return ho jata hai…please kuj kijie…
Ab thik kar diye. Check karo ek baar
Thank you sir 😁