Conquer Life Processes Class 10: Your Essential Q&A Guide (CBSE 2025-26)
Are you gearing up for the upcoming CBSE Class 10 Science exams? Feeling a little apprehensive about Chapter 5: Life Processes? Don't worry, we've got you covered! This blog post serves as your one-stop resource for mastering this crucial chapter.
We've compiled a comprehensive list of important questions and answers that directly align with the CBSE Class 10 Science syllabus (Chapter 5). This guide, meticulously crafted for the 2025-26 academic session, will equip you with a solid foundation for tackling exam questions with confidence.
The best part? We've also prepared a downloadable PDF containing all the questions and answers for your convenience. So, buckle up and get ready to excel in Life Processes!

| Subject | Science (Chemistry) |
| Class | 10 |
| Board | CBSE |
| Chapter No. | 5 |
| Chapter Name | Life Processes |
| Type | Important Questions and Answers |
| Session | 2025-26 |
Life Processes Class 10 Important Questions & Answers
Q. No. 1) Multiple Choice Questions:
i. The labeling for the slide of leaf peel showing stomata by a group of four students who made the diagram and tabulated the labels as follows:
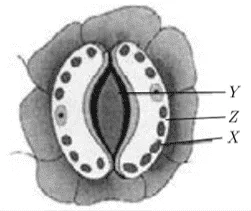
Choose the correct combination of plots provided in the following table.
| X | Y | Z | |
| a. | Chloroplast | Guard cell | Stomatal pore |
| b. | Chloroplast | Stomatal pore | Guard cell |
| c. | Guard cell | Stomatal pore | Chloroplast |
| d. | Stomatal pore | Chloroplast | Guard cell |
Ans. Option (b)
ii. What is the mode of nutrition in fungi?
a. Autotrophic
b. Heterotrophic
c. Saprophytic
d. Parasitic
Ans. Option (b) or (c)
iii. In the given transverse section of the leaf identify the layer of cells where maximum photosynthesis occurs.

a. I, II
b. II, III
c. III, IV
d. I, IV
Ans. Option (b).
iv. Opening and closing of stomatal pore depend on:
a. Atmospheric temperature
b. Oxygen concentration around stomata
c. Carbon dioxide concentration around stomata
d. Water content in the guard cells
Ans. Option (d).
v. Lime water turns cloudy in the presence of a gas which is a by-product of respiration.
Shown below are four setups kept in sunlight for 24 hours.
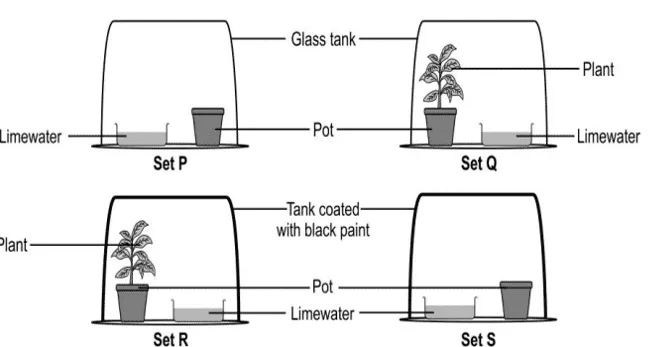
In which setup is lime water expected to be the cloudiest?
a. Setup P
b. Setup Q
c. Setup R
d. Setup S
Ans. Option (c)
vi. Generally food is broken and absorbed within the body of organisms. In which of the following organisms is it done outside the body?
a. Amoeba
b. Mushroom
c. Paramoecium
d. Lice
Ans. Option (b)
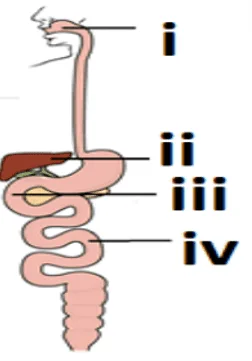
vii. Identify the option that indicates the correct enzyme that is secreted in locations A, B, and C.
a. i. lipase, ii. trypsin, iii. pepsin
b. i. amylase, ii. pepsin, iii. trypsin
c. i. trypsin, ii. amylase, iii. carboxylase
d. i. permease, ii. carboxylase, iii. oxidase
Ans. Option (b).
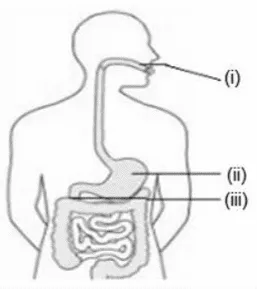
viii. Observe the diagram of the human digestive system.
Match the labeling referred to in column I and correlate it with the function in column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| i. | a. The length of this depends on the food the organism eats. |
| ii. | b. Initial phase of starch digestion. |
| iii. | c. Increases the efficiency of lipase enzyme action. |
| iv. | d. This is the site of the complete digestion of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. |
a) i - a, ii - b, iii – c, iv - d
b) i - b, ii - c, iii – d, iv - a
c) i - b, ii - d, iii – c, iv - a
d) i - d, ii - a, iii – b, iv - c
Ans. Option (b).
ix. Carefully study the diagram of the human respiratory system with labels A, B, C, and D.
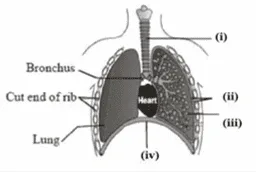
Select the option which gives correct identification and the main function and characteristic.
a. i. Trachea: It is supported by bony rings for conducting inspired air.
b. ii. Ribs: When we breathe out, ribs are lifted.
c. iii. Alveoli: Thin-walled sac-like structures for the exchange of gases.
d. iv. Diaphragm: It is pulled up when we breathe in.
Ans. Option (c).
x. The characteristic processes observed in anaerobic respiration are:
- Presence of oxygen
- Release of carbon dioxide
- Release of energy
- Release of lactic acid
a. i, ii only
b. i, ii, iii only
c. ii, iii, iv only
d. iv only
Ans. Option (c).
xi. Study the table below and select the row that has the incorrect information.
| Aerobic | Anaerobic | |
| a. Location | Cytoplasm | Mitochondria |
| b. End product | CO2 and H2O | Ethanol and CO2 |
| c. Amount of ATP | High | Low |
| d. Oxygen | Needed | Not needed |
Ans. Option (a).
xii. The respiratory route of air in the respiratory tract of humans is:
a. Nostrils → pharynx → larynx → trachea → alveoli.
b. Alveoli → pharynx → larynx → trachea → nostrils.
c. Alveoli → larynx → trachea → pharynx → nostrils.
d. Nostrils → trachea → pharynx → larynx → alveoli.
Ans. Option (a).
xiii. Study the graph below that represents the blood test reports of an athlete just before and after a race.
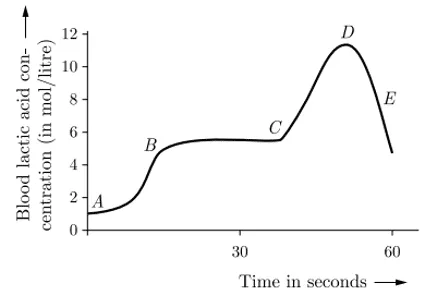
Choose the correct combination of plots provided in the following table.
| Section of race | The concentration of lactic acid | Type of respiration | |
| a. | A - B (sprint start) | Changing high to low | Changing from anaerobic to aerobic |
| b. | B - C (maintaining speed) | High to low | Anaerobic |
| c. | C - D (sprint finish) | High | Aerobic |
| d. | D - E (just after sprint finishing) | Low | Aerobic |
Ans. Option (d).
xiv. Which of the following statement(s) is(are) true about human heart?
- Left atrium receives oxygenated blood from different parts of the body while the right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the lungs.
- Left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to different body parts while the right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
- Left atrium transfers oxygenated blood to the right ventricle which sends it to different parts of the body.
- Right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from different parts of the body while the left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to different parts of the body.
a. i
b. ii
c. ii and iv
d. i and iii
Ans. Option (c).
xv. Identify the phase of circulation which is represented in the diagram of the heart given below. Arrows indicate the contraction of the chambers shown.
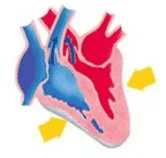
a. Blood transferred to the right ventricle and left ventricle simultaneously.
b. Blood is transferred to the lungs for oxygenation and is pumped into various organs simultaneously.
c. Blood transferred to the right auricle and left auricle simultaneously.
d. Blood is received from the lungs after oxygenation and is received from various organs of the body.
Ans. Option (b).
xvi. The figure given below shows a schematic plan of blood circulation in humans with labels (i) to (iv). Identify the correct label with its functions.
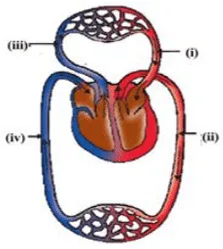
a. i. Pulmonary vein – takes impure blood from the body part.
b. ii. Pulmonary artery – takes blood from the lung to the heart.
c. iii. Aorta – takes blood from the heart to body parts.
d. iv. Vena cava – takes blood from body parts to the right auricle.
Ans. Option (d).
xvii. The doctor measured Ravi’s blood pressure and said it is normal now. The range of Ravi’s blood pressure (systolic/diastolic) is likely to be:
a. 120/80 mm of Hg
b. 160/80 mm of Hg
c. 120/60 mm of Hg
d. 180/80 mm of Hg
Ans. Option (a).
xviii. In which of the following vertebrate groups, the heart does not pump oxygenated blood to different parts of the body?
a. Pisces and amphibians
b. Amphibians and reptiles
c. Amphibians only
d. Pisces only
Ans. Option (d).
xix. Assertion (A): Capillaries have walls that are just one cell thick.
Reason (R): The exchange of material between the blood and surrounding cells takes place across the capillaries.
Options
a. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
b. Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
c. A is true but R is false
d. A is false but R is true
Ans. Option (a)
xx. Look at the diagram below carefully.
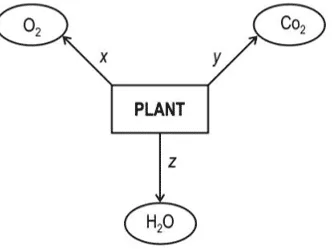
Identify the process taking place at Z.
a. Reproduction
b. Transpiration
c. Photosynthesis
d. Translocation
Ans. Option (b)
Q. No. 2) Case-Based Question
The figure shown below represents an activity to prove the requirements for photosynthesis. During this activity, two healthy potted plants were kept in the dark for 72 hours. After 72 hours, KOH is kept in the watch glass in setup X and not in setup Y. Both these setups are airtight and have been kept in light for 6 hours. Then, the Iodine test is performed with one leaf from each of the two plants X and Y.
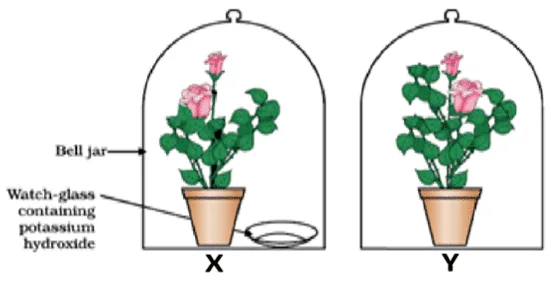
i. This experimental setup is used to prove the essentiality of which of the following requirements of photosynthesis?
a. Chlorophyll
b. Oxygen
c. Carbon dioxide
d. Sunlight
Ans. Option (c).
ii. The function of KOH is to absorb
a. Oxygen
b. Carbon dioxide
c. Moisture
d. Sunlight
Ans. Option (b).
iii. Which of the following statements shows the correct results of the Iodine test performed on the leaf from plant X and Y respectively?
a. Blue-black color would be obtained on the leaf of plant X and no change in color on the leaf of plant Y.
b. Blue-black color would be obtained on the leaf of plant Y and no change in color on the leaf of plant X.
c. Red color would be obtained on the leaf of plant X and brown color on the leaf of plant Y.
d. Red color would be obtained on the leaf of plant Y and brown color on the leaf of plant X.
Ans. Option (b).
iv. Which of the following steps can be followed for making the apparatus airtight?
- Placing the plants on a glass plate
- Using a suction pump
- Applying vaseline to seal the bottom of the jar
- Creating a vacuum
a. i and ii
b. ii and iii
c. i and iii
d. ii and iv
Ans. Option (c).
Q. No. 3) Case-Based Question
Study the picture given above and choose the correct combination of plots provided in the following table:
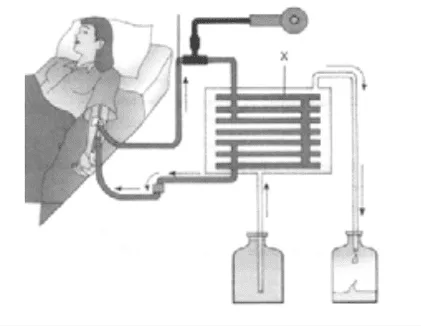
i.
| X | Process Used | Function | |
| a. | Dialyzing pump | Filtration | To draw blood from the body and send it to the dialyzer. |
| b. | Dialysate | Osmosis | To add fluid to the blood. |
| c. | Blood thinner | Clotting | To remove the clots from the blood. |
| d. | Dialyser | Diffusion | To remove the excess wastes and fluid from the blood. |
Ans. Option (d).
ii. Which of the following statement(s) is(are) true about excretion in human beings?
- Urine is stored in the urethra until the urge of passing it out.
- Each kidney has large numbers of filtration units called nephrons.
- The bladder is muscular, so it is under nervous control.
- Kidneys are the primary excretory organs.
a. i and ii only
b. i and iii only
c. ii, iii, and iv only
d. i and iv only
Ans. Option (c).
iii. The given figure represents the structure of a nephron.
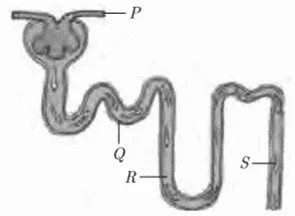
Which section of the nephron is responsible for concentrating the solute in the filtrate?
a. P
b. Q
c. R
d. S
Ans. Option (c).
iv. The excretory system of human beings includes
a. A kidney, a ureter, a urinary bladder, and a urethra
b. A pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, a pair of urinary bladders, and a urethra
c. A pair of kidneys, a pair of urinary bladders, a ureter, and a urethra
d. A pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra
Ans. Option (d).
Q. No. 4) Fill in the blanks:
i. Ultra filtration takes place in ______ of the nephron.
ii. ______ is involved in the breakdown of glucose to produce energy for metabolic activities in a cell.
iii. Blood from the superior vena cava flows into _______.
Ans. i. Bowman’s capsule
ii. Mitochondria
iii. right atrium
Q. No. 5) i. Match the terms in Column (A) with those in Column (B):
| Column A | Column B |
| a. Trypsin | i. Pancreas |
| b. Amylase | ii. Liver |
| c. Bile | iii. Gastric glands |
| d. Pepsin | iv. Saliva |
Ans. a → i, b → iv, c → ii, d → iii.
ii. Match the terms in Column (A) with those in Column (B):
| Column A | Column B |
| a. Phloem | i. Excretion |
| b. Nephron | ii. Translocation of food |
| c. Veins | iii. Clotting of blood |
| d. Platelets | iv. Deoxygenated blood |
Ans. a → ii, b → i, c → iv, d → iii.
iii. Match the terms in Column (A) with those in Column (B):
| Column A | Column B |
| a. Autotrophic nutrition | i. Leech |
| b. Heterotrophic nutrition | ii. Paramecium |
| c. Parasitic nutrition | iii. Deer |
| d. Digestion in food vacuoles | iv. Green plant |
Ans. a → iv, b → iii, c → i, d → ii.
Q. No. 6) Name the following:
i. The process in plants that links light energy with chemical energy.
ii. Organisms that can prepare their own food.
iii. The cell organelle where photosynthesis occurs.
iv. Cells that surround a stomatal pore.
v. Organisms that cannot prepare their own food.
vi. An enzyme secreted from gastric glands in the stomach that acts on proteins.
vii. The universal source of energy in all cells.
Ans. i. Photosynthesis
ii. Autotrophs.
iii. Chloroplast.
iv. Guard cells.
v. Heterotrophs.
vi. Pepsin.
vii. ATP (Adenosine Tri Phosphate).
Q. No. 7) Why is nutrition a necessity for an organism?
Ans. Food is required for the following purposes:
- It provides energy for the various metabolic processes in the body.
- It is essential for the growth of new cells and the repair or replacement of worn-out cells.
- It is needed to develop resistance against various diseases.
Q. No. 8) What is the meaning of variegated leaf?
Ans. The variegated leaf means a leaf with some green and some non-green parts.
Q. No. 9) List two factors that decide the direction of diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Ans. Environmental conditions and requirements of the plants decide the direction of diffusion of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Q. No. 10) The leaves of a plant were covered with aluminium foil, how would it affect the physiology of the plant?
Ans. i. No photosynthesis will occur so no glucose will be made. Also, no respiration will take place as no oxygen will be taken in.
ii. No transpiration will occur so there would be no upward movement of water or minerals from the soil as there will be no transpirational pull.
iii. Temperature regulation of the leaf surface will be affected.
Q. No. 11) State the events occurring during the process of photosynthesis. Is it essential that these steps take place one after the other immediately?
Ans. Events occurring during the process of photosynthesis:
- Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll.
- Conversion of light energy to chemical energy.
- Splitting of water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates.

These steps need not take place one after the other immediately. For example, desert plants take up carbon dioxide at night and prepare an intermediate which is acted upon by the energy absorbed by the chlorophyll during the day.
Q. No. 12) “All plants give out oxygen during the day and carbon dioxide during the night.” Do you agree with this statement? Give reason.
Ans. During day time, as the rate of photosynthesis is more than the rate of respiration, the net result is the evolution of oxygen. At night there is no photosynthesis, so they give out carbon dioxide due to respiration.
Q. No. 13) If a plant is releasing carbon dioxide and taking in oxygen during the day, does it mean that there is no photosynthesis occurring? Justify your answer.
Ans. The release of carbon dioxide and intake of oxygen gives evidence that either photosynthesis is not taking place or its rate is too low. Normally during day time, the rate of photosynthesis is much more than the rate of respiration. So, carbon dioxide produced during respiration is used up for photosynthesis hence carbon dioxide is not released.
Q. No. 14) Enlist the site of synthesis and storage of bile. ‘Bile juice does not have any digestive enzyme but still plays a significant role in the process of digestion.’ Justify the statement.
Ans. Site of synthesis: Liver
Site of storage: Gall bladder.
Bile juice does not contain any digestive enzyme, but it plays an important role in digestion because:
- The bile salts emulsify fat by acting on large fat globules to break them into smaller globules. This increases the efficiency of pancreatic enzymes.
- The food entering the small intestine is acidic. It is made alkaline by the action of bile juice so as to facilitate the action of pancreatic enzymes.
Q. No. 15) Out of a goat and a tiger, which one will have a longer small intestine? Justify your answer.
Ans. Goat, because herbivorous eating grass needs a longer small intestine to allow the cellulose to be digested.
Q. No. 16) A person suffering from liver disease is advised to avoid fatty and highly acidic foods.
Give a reason why each of the foods mentioned should be avoided by a person suffering from liver disease.
Ans. i. Since the liver produces bile which creates an alkaline medium for effective digestion, in absence of bile acidic foods may cause more acidity and poor digestion.
ii. Since bile is responsible for fat digestion by converting large fat globules to smaller ones for efficient digestion, in absence of which fats will not be properly digested.
Q. No. 17) State the role of the pancreas in the digestion of food.
Ans. The pancreas secretes digestive juice which contains enzymes like trypsin for digesting proteins and lipase for the breakdown of emulsified fats.
Q. No. 18) How is the wall of the small intestine adapted for performing the function of absorption of food?
Ans. The inner lining of the small intestine has numerous finger-like projections called villi which increase the surface area for absorption.
Q. No. 19) What are the components of gastric juice? Write their functions.
Ans. Gastric juice contains three components:
- Hydrochloric acid: Hydrochloric acid in the stomach is used to make the medium acidic to facilitate the action of the enzyme pepsin and to kill germs if any.
- Enzyme pepsin: It digests proteins to convert them into peptones.
- Mucus: It helps to protect the stomach wall from its own secretions of hydrochloric acid.
Q. No. 20) Show the breakdown of glucose by various pathways.
Ans.
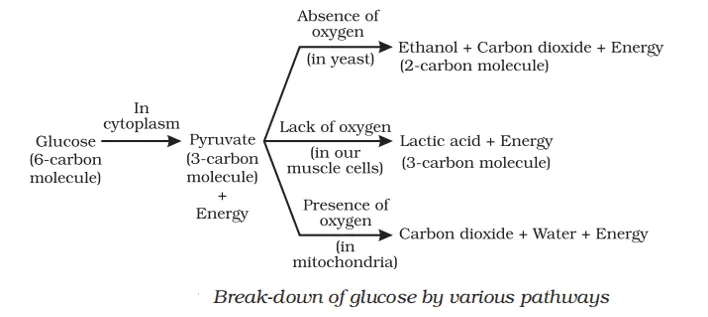
Q. No. 21) What are the end products formed during fermentation in yeast? Under what conditions a similar process takes place in our body that leads to muscle cramps?
Ans. The end products formed during anaerobic respiration or fermentation in yeast are carbon dioxide and ethanol along with ATP.
A similar process is seen in our body when there is a lack of oxygen in the muscles, leading to muscle fatigue. It results due to the accumulation of lactic acid produced during the anaerobic respiration of glucose. The energy or ATP produced during anaerobic respiration is much less as compared to aerobic respiration.
Q. No. 22) What is the role of cartilaginous rings on the trachea?
Ans. They prevent the collapsing of the trachea when there is no air present in it.
Q. No. 23) Elucidate the process of the double circulatory system with the help of a diagram.
Ans.
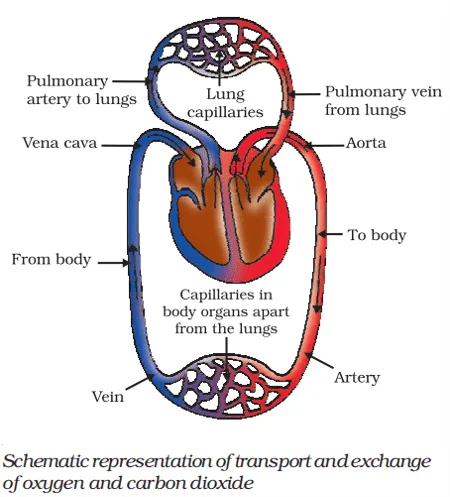
The oxygenated blood from the lungs returns to the heart, which is pumped again into different parts of the body by the heart. Thus, the blood passed twice through the heart making one complete round through the body, i.e., once through the right half in the form of deoxygenated blood and once through the left half in the form of oxygenated blood.
Q. No. 24) Oxygen, mostly, is carried by a pigment in our blood whereas carbon dioxide is transported in dissolved form in our blood.
Give TWO reasons that make the above statement correct.
Ans. i. Carbon dioxide is more soluble in water than oxygen.
ii. Haemoglobin (the red pigment in RBC) has a very high affinity for oxygen.
Q. No. 25) Given below is a table representing the characteristics of two fluids involved in the transportation of substances in the human body.
| Fluid A | Fluid B |
| Colorless | Colored |
| Contains less oxygen | Contains more oxygen |
| Contains less protein | Contains more protein |
i. Identify fluid A and fluid B.
ii. With the help of a flow chart, describe the movement of fluid A from the intercellular spaces to the main circulatory system.
Ans. i. Fluid A – Lymph
Fluid B – Blood
ii. Intercellular spaces → Lymphatic capillaries → Lymph vessels → Larger veins.
Q. No. 26) How is lymph an important fluid involved in transportation? If lymphatic vessels get blocked, how would it affect the human body? Elaborate.
Ans. The functions of lymph in transportation are:
- Lymph carries digested and absorbed fat from the intestine back to the blood.
- Lymph drains excess fluid from extracellular space back into the blood.
Blockage of the lymphatic system will lead to water retention and poor fat absorption in the body.
Q. No. 27) What are the strategies of plants to get rid of their wastes?
Ans. Strategies of plants to get rid of their waste are:
- They throw away oxygen and water vapor through stomata.
- Some wastes like gums, oil, and resins may be stored in old xylem or wood in the stem.
- Some wastes may be stored in leaves and bark and shed off from time to time.
- Roots can also throw some waste.
Q. No. 28) Two major forces help in the transport of water in a plant. Force A is the driving force in the movement of water during the day, whereas force B helps the movement of water in a plant during the night or during the day when humidity is very high.
i. Identify force A and force B.
ii. Describe how each of these forces helps in the movement of water in a plant.
Ans. i. Force A – transpirational pull
Force B – Root pressure
ii. Transpiration pull: Evaporation of water molecules from the stomata of a leaf due to transpiration creates a suction that pulls water from the xylem cells of roots.
Root pressure: Active absorption of ions by roots from the soil causes water to steadily move into the root xylem creating a column of water that is pushed upwards.
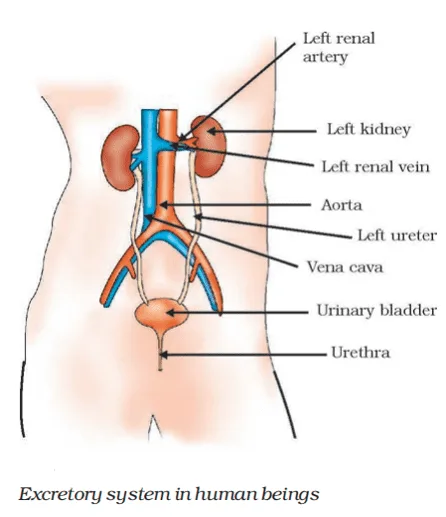
Q. No. 29) a. Define excretion.
b. Name the basic filtration unit present in the kidney.
c. What is the purpose of making urine in the human body?
d. Draw the excretory system in human beings and label the following organs of the excretory system which perform the following functions:
i. Forms urine.
ii. Is a long tube that collects urine from the kidney.
iii. Stores urine until it is passed out.
iv. Releases urine.
Ans. a. Throwing out wastes from the living body is called excretion.
b. Nephron.
c. To filter out nitrogenous waste products like urea and uric acid from the blood in humans.
d. i. Kidney, ii. Ureter, iii. Urinary bladder, iv. Urethra
Q. No. 30) Give reason:
i. Separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is necessary for mammals.
ii. The rate of breathing in a fish is faster than a pigeon.
iii. We experience pain in our muscles after strenuous physical exercise.
iv. Veins are thin-walled and have valves.
v. In birds and mammals the left and right sides of the heart are separated.
vi. Patients whose gallbladder is removed are recommended to eat less oily food.
vii. Absorption of digested food occur mainly in the small intestine.
Ans. i. Mammals are warm-blooded hence a lot of energy is required to maintain a constant body temperature.
ii. A fish breathes in oxygen dissolved in water and the percentage of oxygen dissolved in water is less as compared to the atmosphere.
iii. Due to a lack of oxygen anaerobic respiration occurs resulting in the formation of lactic acid. Accumulation of lactic acid causes pain in the muscles.
iv. Veins have thin walls because the blood there is no longer under pressure and they have valves to ensure blood flow in one direction.
v. The separation keeps oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from mixing allowing a highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body. This is useful in animals that have high energy needs (birds and mammals) and constantly use energy to maintain their body temperature.
vi. Gallbladder stores bile which helps in the emulsification of lipids. In the absence of stored bile, emulsification of fats will be less, and thus fat digestion will be slow. Hence there are such diet restrictions.
vii. Maximum absorption occurs in the small intestine because:
- Digestion is completed in the small intestine.
- The inner lining of the small intestine is provided with villi which increases the surface area for absorption.
- The wall of the intestine is richly supplied with blood vessels (which take the absorbed food to each and every cell of the body).
Q. No. 31) Differentiate between:
i. Saprophytic Nutrition and Parasitic Nutrition
ii. Aerobic Respiration and Anaerobic Respiration
iii. Autotroph and Heterotroph
iv. Artery and Vein
v. Blood and Lymph
Ans. i.
| Saprophytic nutrition | Parasitic nutrition |
| 1. Taking dead decaying organic matter in the form of food is called saprophytic nutrition. | 1. Living on or inside other organisms and deriving their food from them without killing them is called parasitic nutrition. |
| 2. It does not depend on a living host. | 2. It causes harm to the organism. |
| 3. Example: fungi like bread moulds, yeast, and mushrooms. | 3. Example: Cuscuta (Amar-bel), ticks, lice, leeches, and tapeworms. |
ii.
| Aerobic respiration | Anaerobic respiration |
| 1. Takes place in the presence of oxygen. | 1. Takes place in the absence of oxygen. |
| 2. Complete breakdown of food occurs in it. | 2. Incomplete breakdown of food occurs in it. |
| 3. The end products are Carbon dioxide and water. | 3. The end products are lactic acid or ethanol and Carbon dioxide. |
| 4. It takes place in the cytoplasm and inside mitochondria. | 4. It takes place in the cytoplasm only. |
| 5. More energy is released. | 5. Less energy is released. |
iii.
| Autotroph | Heterotroph |
| 1. Organisms that prepare their own food. | 1. Organisms that are dependent on other organisms for food. |
| 2. They have chlorophyll. | 2. They lack chlorophyll. |
| 3. Example: Green plants and some bacteria. | 3. Example: Animals and fungi. |
iv.
| Artery | Vein |
| 1. Have thick, elastic, muscular walls. | 1. Have thin, non-elastic walls. |
| 2. Lumen is narrow. | 2. Lumen is wide. |
| 3. Carry blood from the heart to all body parts. | 3. Carry blood from all body parts to the heart. |
| 4. Carry oxygenated blood (except pulmonary artery). | 4. Carry deoxygenated blood (except pulmonary vein). |
| 5. Has high blood pressure. | 5. Has low blood pressure. |
v.
| Blood | Lymph |
| 1. Red in color. | 1. Colorless. |
| 2. RBCs are present. | 2. RBCs are absent. |
| 3. Nutritive substances are more. | 3. Nutritive substances are less. |
| 4. Contains more oxygen. | 4. Contains less oxygen. |
| 5. Contains more protein. | 5. Contains less protein. |
| 6. Metabolic wastes and Carbon dioxide are in normal amounts. | 6. Both are more than blood. |
| Must Read: Life Processes Class 10 Notes: Simplified and Easy to Understand Life Process Class 10 MCQ Test |
Hope these questions were helpful to you in preparing for CBSE Class 10 board exams. Do comment if you have any questions/doubts or help me know your requirements.


Please Create and provide pdf for us 🙏🏻
This is better than PDFs because PDF downloads would be lost in your device. But here in website you can get everything at one place. You can also take printout of entire page.
You are right sir
Hey sir !
it me prashant kumar raj
Sir i wanted to know that all these questions of this chapter are enough for the class 10 board preparation!
Or any more questions i have to do
Please provide me your contact number (VERY URGENT)sir please
Please dont say NO!
Bye!!!
Your student
Prashant Kumar Raj(X)
School- I dont go school because of some family relalted problems!
Prepare all these questions thoroughly. And don’t worry about anything.
Sir how to read ncert like you ?
Just keep trying, you’ll be reading better than me.
Sir i have one dout that if i only learn your given question answer then it will enough to get good marks
Yes, but it also depends on how well you prepare these questions and understand the concepts behind these questions.
Hey, sir
Whether previous year question is included in this important questions or not
Sir thanks for important question
Always welcome
Sir, in Q2 of life processes the correct answer is option(c).
Actually both (b) and (c) are correct. Saprophytic nutrition is a type of heterotrophic nutrition.
Sir it is really helpful
Sir can you give explanation too
Really helpful. Nice questions
Glad it was helpful. Also check other chapters questions
I think 10 th question answer is wrong
Sry my mistake
Sir question 4 answer 1 is bowman’s capsule
Correction done 👍
Sir these questions will be coming in cbse delhi board 2025
Yes these are for CBSE board only.
Sir can I prepare these questions for board 2025
Sir can I prepare these questions for board 2025
Absolutely yes
Hello sir these questions sample paper and ncert reading is enough for 2025 exam
Recently found your channel sir and since then my fear of exams is reduced.
Thanks a lot sir 🙏❤️